Liraglutide
Vue d'ensemble
Description
Le liraglutide est un analogue synthétique du peptide-1 de type glucagon humain, principalement utilisé dans le traitement du diabète de type 2 et de l’obésité . Il est commercialisé sous les noms de marque Victoza et Saxenda . Le this compound imite l’action de l’hormone naturelle peptide-1 de type glucagon, qui contribue à réguler la glycémie et l’appétit .
Mécanisme D'action
Le liraglutide exerce ses effets en agissant comme un agoniste du récepteur du peptide-1 de type glucagon . Ce récepteur est impliqué dans la régulation de la sécrétion d’insuline, de la libération de glucagon et de l’appétit . En activant ce récepteur, le this compound améliore la sécrétion d’insuline, inhibe la libération de glucagon, ralentit la vidange gastrique et réduit l’apport alimentaire .
Applications De Recherche Scientifique
Liraglutide has a wide range of scientific research applications:
Chemistry: Used as a model peptide for studying peptide synthesis and modification techniques.
Biology: Investigated for its role in regulating glucose metabolism and appetite.
Medicine: Extensively studied for its therapeutic effects in type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Industry: Used in the development of new peptide-based therapeutics.
Analyse Biochimique
Biochemical Properties
Liraglutide plays a significant role in biochemical reactions. It interacts with various enzymes, proteins, and other biomolecules. For instance, it has been found to interact with glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP-1R), which is a G protein-coupled receptor . The nature of these interactions involves binding to the receptor, which triggers a series of biochemical reactions leading to the secretion of insulin .
Cellular Effects
This compound has profound effects on various types of cells and cellular processes. It influences cell function by impacting cell signaling pathways, gene expression, and cellular metabolism. For instance, it has been found to preserve pancreatic beta cells via regulation of cell kinetics and suppression of oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress in a mouse model of diabetes .
Molecular Mechanism
The mechanism of action of this compound is quite complex. It exerts its effects at the molecular level through binding interactions with biomolecules, enzyme inhibition or activation, and changes in gene expression. For instance, it binds to the GLP-1R, which leads to the activation of adenylyl cyclase and an increase in cyclic AMP levels .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, the effects of this compound change over time. It has been found to have a half-life of more than 13 hours, indicating its stability . Long-term effects on cellular function observed in in vitro or in vivo studies include improved insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of this compound vary with different dosages in animal models. For instance, in db/db mice, this compound treatment improved metabolic variables and insulin sensitivity .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound is involved in several metabolic pathways. It interacts with enzymes such as adenylyl cyclase and influences metabolic flux and metabolite levels .
Transport and Distribution
This compound is transported and distributed within cells and tissues. It is administered as an isotonic solution by subcutaneous injection .
Subcellular Localization
Given its role in activating the GLP-1R, it is likely that it is localized to the cell membrane where this receptor is found .
Méthodes De Préparation
Voies synthétiques et conditions de réaction
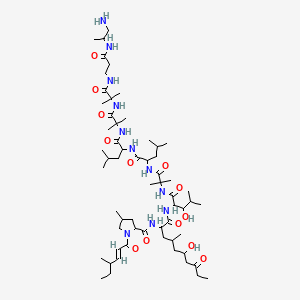
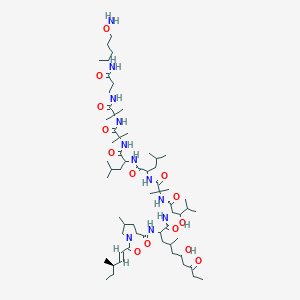
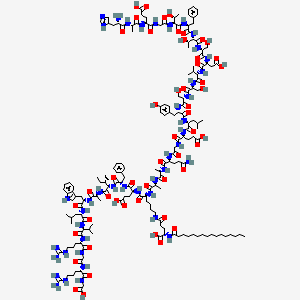
Le liraglutide est synthétisé en attachant un acide gras en C-16 (acide palmitique) avec un espaceur d’acide glutamique au résidu lysine en position 26 du précurseur peptidique . La synthèse implique des techniques de synthèse peptidique en phase solide, où les acides aminés sont ajoutés séquentiellement à une chaîne peptidique croissante ancrée à une résine solide . Le produit final est ensuite clivé de la résine et purifié par chromatographie liquide haute performance .
Méthodes de production industrielle
La production industrielle du this compound implique une synthèse peptidique en phase solide à grande échelle suivie d’une purification par des techniques chromatographiques . Le processus est optimisé pour garantir un rendement élevé et une pureté du produit final, ce qui est essentiel pour son efficacité thérapeutique .
Analyse Des Réactions Chimiques
Types de réactions
Le liraglutide subit diverses réactions chimiques, notamment :
Oxydation : Le this compound peut être oxydé au niveau des résidus méthionine, ce qui peut affecter sa stabilité et son activité.
Réduction : Les réactions de réduction sont moins fréquentes mais peuvent se produire dans des conditions spécifiques.
Réactifs et conditions courants
Oxydation : Le peroxyde d’hydrogène ou d’autres agents oxydants peuvent être utilisés dans des conditions contrôlées.
Réduction : Des agents réducteurs comme le dithiothréitol peuvent être utilisés.
Substitution : Divers réactifs chimiques peuvent être utilisés pour introduire des substitutions à des résidus spécifiques.
Principaux produits formés
Les principaux produits formés à partir de ces réactions comprennent des formes oxydées ou réduites de this compound, qui peuvent avoir des propriétés pharmacologiques différentes .
Applications de la recherche scientifique
Le this compound a une large gamme d’applications de recherche scientifique :
Chimie : Utilisé comme peptide modèle pour étudier les techniques de synthèse et de modification des peptides.
Biologie : Étudié pour son rôle dans la régulation du métabolisme du glucose et de l’appétit.
Médecine : Étudié de manière approfondie pour ses effets thérapeutiques dans le diabète de type 2 et l’obésité.
Industrie : Utilisé dans le développement de nouvelles thérapies à base de peptides.
Comparaison Avec Des Composés Similaires
Composés similaires
Sémaglutide : Un autre agoniste du récepteur du peptide-1 de type glucagon utilisé pour des indications similaires.
Exénatide : Un agoniste du récepteur du peptide-1 de type glucagon à action plus courte.
Dulaglutide : Un agoniste du récepteur du peptide-1 de type glucagon à action prolongée.
Unicité
Le liraglutide est unique en raison de son schéma posologique une fois par jour et de sa capacité à réduire considérablement le poids corporel en plus d’améliorer le contrôle glycémique . Contrairement à certains autres agonistes du récepteur du peptide-1 de type glucagon, le this compound a montré des effets bénéfiques sur les résultats cardiovasculaires .
Propriétés
IUPAC Name |
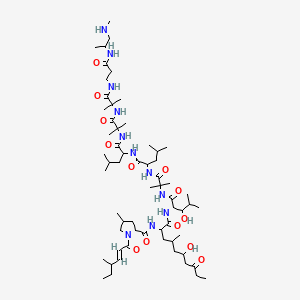
(2S)-5-[[(5S)-5-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-5-amino-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S,3R)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S,3R)-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-amino-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)propanoyl]amino]propanoyl]amino]-4-carboxybutanoyl]amino]acetyl]amino]-3-hydroxybutanoyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxybutanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-3-carboxypropanoyl]amino]-3-methylbutanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoyl]amino]-4-methylpentanoyl]amino]-4-carboxybutanoyl]amino]acetyl]amino]-5-oxopentanoyl]amino]propanoyl]amino]propanoyl]amino]-6-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S,3S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-5-carbamimidamido-1-[[2-[[(2S)-5-carbamimidamido-1-(carboxymethylamino)-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]amino]-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-4-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl]amino]-4-carboxy-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-6-oxohexyl]amino]-2-(hexadecanoylamino)-5-oxopentanoic acid | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C172H265N43O51/c1-18-20-21-22-23-24-25-26-27-28-29-30-37-53-129(224)195-116(170(265)266)59-64-128(223)180-68-41-40-50-111(153(248)199-115(62-67-135(232)233)154(249)204-120(73-100-44-33-31-34-45-100)159(254)214-140(93(11)19-2)167(262)192-97(15)146(241)201-122(76-103-79-183-108-49-39-38-48-106(103)108)157(252)203-118(72-90(5)6)158(253)212-138(91(7)8)165(260)200-110(52-43-70-182-172(177)178)149(244)184-81-130(225)193-109(51-42-69-181-171(175)176)148(243)187-84-137(236)237)196-144(239)95(13)189-143(238)94(12)191-152(247)114(58-63-127(174)222)194-131(226)82-185-151(246)113(61-66-134(230)231)198-155(250)117(71-89(3)4)202-156(251)119(75-102-54-56-105(221)57-55-102)205-162(257)124(85-216)208-164(259)126(87-218)209-166(261)139(92(9)10)213-161(256)123(78-136(234)235)206-163(258)125(86-217)210-169(264)142(99(17)220)215-160(255)121(74-101-46-35-32-36-47-101)207-168(263)141(98(16)219)211-132(227)83-186-150(245)112(60-65-133(228)229)197-145(240)96(14)190-147(242)107(173)77-104-80-179-88-188-104/h31-36,38-39,44-49,54-57,79-80,88-99,107,109-126,138-142,183,216-221H,18-30,37,40-43,50-53,58-78,81-87,173H2,1-17H3,(H2,174,222)(H,179,188)(H,180,223)(H,184,244)(H,185,246)(H,186,245)(H,187,243)(H,189,238)(H,190,242)(H,191,247)(H,192,262)(H,193,225)(H,194,226)(H,195,224)(H,196,239)(H,197,240)(H,198,250)(H,199,248)(H,200,260)(H,201,241)(H,202,251)(H,203,252)(H,204,249)(H,205,257)(H,206,258)(H,207,263)(H,208,259)(H,209,261)(H,210,264)(H,211,227)(H,212,253)(H,213,256)(H,214,254)(H,215,255)(H,228,229)(H,230,231)(H,232,233)(H,234,235)(H,236,237)(H,265,266)(H4,175,176,181)(H4,177,178,182)/t93-,94-,95-,96-,97-,98+,99+,107-,109-,110-,111-,112-,113-,114-,115-,116-,117-,118-,119-,120-,121-,122-,123-,124-,125-,126-,138-,139-,140-,141-,142-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
YSDQQAXHVYUZIW-QCIJIYAXSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)NC(CCC(=O)NCCCCC(C(=O)NC(CCC(=O)O)C(=O)NC(CC1=CC=CC=C1)C(=O)NC(C(C)CC)C(=O)NC(C)C(=O)NC(CC2=CNC3=CC=CC=C32)C(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C(=O)NC(C(C)C)C(=O)NC(CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)NCC(=O)NC(CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)NCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)N)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC4=CC=C(C=C4)O)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(C(C)O)NC(=O)C(CC5=CC=CC=C5)NC(=O)C(C(C)O)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(CC6=CN=CN6)N)C(=O)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)N[C@@H](CCC(=O)NCCCC[C@@H](C(=O)N[C@@H](CCC(=O)O)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC1=CC=CC=C1)C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](C)CC)C(=O)N[C@@H](C)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC2=CNC3=CC=CC=C32)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC(C)C)C(=O)N[C@@H](C(C)C)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@@H](CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)NCC(=O)O)NC(=O)[C@H](C)NC(=O)[C@H](C)NC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)N)NC(=O)CNC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CC(C)C)NC(=O)[C@H](CC4=CC=C(C=C4)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CO)NC(=O)[C@H](CO)NC(=O)[C@H](C(C)C)NC(=O)[C@H](CC(=O)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CO)NC(=O)[C@H]([C@@H](C)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CC5=CC=CC=C5)NC(=O)[C@H]([C@@H](C)O)NC(=O)CNC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)[C@H](C)NC(=O)[C@H](CC6=CN=CN6)N)C(=O)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C172H265N43O51 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID60174433 | |
| Record name | Liraglutide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60174433 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
3751 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Liraglutide is an acylated synthetic glucagon-like peptide-1 analog. Liraglutide is an agonist of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor which is coupled to adenylate cyclase. The increase in cyclic AMP stimulates the glucose dependant release of insulin, inhibits the glucose dependant release of glucagon, and slows gastric emptying to increase control of blood sugar., Liraglutide is an acylated, long-acting, human glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist; the synthetic (recombinant DNA origin) peptide precursor of liraglutide has 97% amino acid sequence homology to endogenous human GLP-1-(7-37). Liraglutide is prepared by attaching palmitic acid with a glutamic acid spacer on the lysine residue at position 26 of the peptide precursor. GLP-1-(7-37) represents less than 20% of total circulating endogenous GLP-1. Like GLP-1-(7-37), liraglutide activates the GLP-1 receptor in pancreatic beta cells. Liraglutide also increases intracellular cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) leading to insulin release in the presence of elevated glucose concentrations. This insulin secretion subsides as blood glucose concentrations decrease and approach euglycemia. In addition, liraglutide suppresses glucagon secretion in a glucose-dependent manner but does not impair normal glucagon response to hypoglycemia. Liraglutide delays gastric emptying, reducing the rate at which postprandial glucose appears in the circulation. As a result of these actions resulting in increased insulin secretion, suppression of glucagon secretion, and delays in gastric emptying, liraglutide effectively reduces fasting and postprandial plasma glucose concentrations in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus., Liraglutide is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) mimetic used for the treatment of Type 2 diabetes. Similar to the actions of endogenous GLP-1, liraglutide potentiates the post-prandial release of insulin, inhibits glucagon release and increases satiety. Recent epidemiological studies and clinical trials have suggested that treatment with GLP-1 mimetics may also diminish the risk of cardiovascular disease in diabetic patients. The mechanism responsible for this effect has yet to be determined; however, one possibility is that they might do so by a direct effect on vascular endothelium. Since low grade inflammation of the endothelium is an early event in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), we determined the effects of liraglutide on inflammation in cultured human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs). Liraglutide reduced the inflammatory responses to TNFalpha and LPS stimulation, as evidenced by both reduced protein expression of the adhesion molecules VCAM-1 and E-Selectin, and THP-1 monocyte adhesion. This was found to result from increased cell Ca2+ and several molecules sensitive to Ca2+ with known anti inflammatory actions in endothelial cells, including CaMKKbeta, CaMKI, AMPK, eNOS and CREB. Treatment of the cells with STO-609, a CaMKK inhibitor, diminished both the activation of AMPK, CaMKI and the inhibition of TNFa and LPS-induced monocyte adhesion by liraglutide. Likewise, expression of an shRNA against AMPK nullified the anti-inflammatory effects of liraglutide. The results indicate that liraglutide exerts a strong anti-inflammatory effect on HAECs. They also demonstrate that this is due to its ability to increase intracellular Ca2+ and activate CAMKKbeta, which in turn activates AMPK., In vivo, liraglutide lowers blood glucose and body weight in a number of diabetic and obese models using rodents, pigs and monkeys. The mechanism of action in vivo involved glucose-dependent increase in insulin secretion, lowered glucagon secretion, decreased gastric emptying, loss of body fat, lowered food intake, altered food preference, and maintained energy expenditure. The mechanism of action is consistent with a specific GLP-1 effect., Liraglutide is a long-acting GLP-1 analogue, designed to bind to albumin as the main molecular mechanism of protraction. In vitro, this was shown in the receptor cAMP as well as binding assay where addition of albumin right-shifted the dose-response and/or binding curve. The apparent reduced potency of liraglutide underlines that only the free fraction of liraglutide is responsible for its pharmacological effect in vitro as well as in vivo. Furthermore, liraglutide in a pharmaceutical solution forms a micell-like heptamer which may contribute to the slow absorption from the subcutis. | |
| Record name | Liraglutide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB06655 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Liraglutide | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/8205 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
CAS No. |
204656-20-2 | |
| Record name | Liraglutide [USAN:INN:BAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0204656202 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Liraglutide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB06655 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Liraglutide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60174433 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Liraglutide (2S)-5-[[(5S)-5-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-5-amino-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2- [[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S,3R)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S,3R)-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-amino-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl) propanoyl]amino]propanoyl]amino]-4-carboxybutanoyl]amino]acetyl]amino]-3-hydroxybutanoyl]amino]-3- phenylpropanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxybutanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-3-carboxypropanoyl]amino]- 3-methylbutanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl) propanoyl]amino]-4-methylpentanoyl]amino]-4-carboxybutanoyl]amino]acetyl]amino] 5 oxopentanoyl]amino] propanoyl]amino]propanoyl]amino]-6-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S,3S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)- 5-carbamimidamido-1-[[2-[[(2S)-5-carbamimidamido-1-(carboxymethylamino)-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-2- oxoethyl]amino]-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-4-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl] amino]-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl] amino]-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl]amino]-4-carboxy-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-6-oxohexyl]amino]-2- (hexadecanoylamino)-5-oxopentanoic acid | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | Liraglutide | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/8205 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Avertissement et informations sur les produits de recherche in vitro
Veuillez noter que tous les articles et informations sur les produits présentés sur BenchChem sont destinés uniquement à des fins informatives. Les produits disponibles à l'achat sur BenchChem sont spécifiquement conçus pour des études in vitro, qui sont réalisées en dehors des organismes vivants. Les études in vitro, dérivées du terme latin "in verre", impliquent des expériences réalisées dans des environnements de laboratoire contrôlés à l'aide de cellules ou de tissus. Il est important de noter que ces produits ne sont pas classés comme médicaments et n'ont pas reçu l'approbation de la FDA pour la prévention, le traitement ou la guérison de toute condition médicale, affection ou maladie. Nous devons souligner que toute forme d'introduction corporelle de ces produits chez les humains ou les animaux est strictement interdite par la loi. Il est essentiel de respecter ces directives pour assurer la conformité aux normes légales et éthiques en matière de recherche et d'expérimentation.


![(2S)-N-[(4S,6S)-4-amino-7-(3-aminopropanoyl)-6-formyl-9-hydroxy-2,11-dimethyl-5,8-dioxo-7-phenyldodecan-6-yl]-2-hydroxy-N,4-dimethylpent-4-enamide](/img/structure/B1674780.png)
![16-[4-[4-(4,5-dihydroxy-3-methoxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl)oxy-2-hydroxy-5-methyl-6-propan-2-yloxan-2-yl]-3-hydroxypentan-2-yl]-8-hydroxy-3,15-dimethoxy-5,7,9,11-tetramethyl-1-oxacyclohexadeca-3,5,11,13-tetraen-2-one](/img/structure/B1674781.png)
![[(3aS,4S,5R,6Z,10Z,11aR)-3a,4-dihydroxy-6,10-dimethyl-3-methylidene-2-oxo-5,8,9,11a-tetrahydro-4H-cyclodeca[b]furan-5-yl] 2-methylpropanoate](/img/structure/B1674782.png)