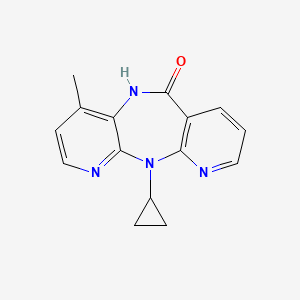
Nevirapin
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Nevirapin ist ein nicht-nukleosidischer Reverse-Transkriptase-Hemmer, der hauptsächlich zur Behandlung und Vorbeugung von Infektionen mit dem Humanen Immundefizienzvirus Typ 1 (HIV-1) eingesetzt wird. Es wird oft in Kombination mit anderen antiretroviralen Medikamenten verwendet, um seine Wirksamkeit zu erhöhen. This compound wirkt, indem es das Reverse-Transkriptase-Enzym hemmt, das für die Replikation von HIV-1 entscheidend ist .
2. Herstellungsmethoden
Synthesewege und Reaktionsbedingungen: this compound kann durch verschiedene Methoden synthetisiert werden, darunter die Kondensation von 2-Chlor-3-cyanopyridin mit Cyclopropylamin, gefolgt von Cyclisierung und Methylierung. Die Reaktionsbedingungen umfassen typischerweise die Verwendung von Lösungsmitteln wie Dimethylformamid und Katalysatoren wie Kaliumcarbonat .
Industrielle Produktionsmethoden: Die industrielle Produktion von this compound beinhaltet oft die großtechnische Synthese unter Verwendung ähnlicher chemischer Wege, die jedoch für höhere Ausbeuten und Reinheit optimiert sind. Techniken wie Hochdruckhomogenisierung und Nanosuspensionsherstellung werden eingesetzt, um die Löslichkeit und Bioverfügbarkeit der Verbindung zu verbessern .
Wirkmechanismus
Target of Action
Nevirapine is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) with activity against Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 (HIV-1) . Its primary target is the reverse transcriptase enzyme, an essential viral enzyme which transcribes viral RNA into DNA .
Mode of Action
Nevirapine binds directly to reverse transcriptase and blocks the RNA-dependent and DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activities by causing a disruption of the enzyme’s catalytic site .
Biochemical Pathways
Nevirapine’s action affects the biochemical pathway of viral replication. By binding to the reverse transcriptase enzyme, it inhibits the transcription of viral RNA into DNA, thereby preventing the replication of the virus .
Pharmacokinetics
Nevirapine has a bioavailability of 93% ± 9% . It is metabolized in the liver and has an elimination half-life of 45 hours . Less than 6% of the parent drug is excreted via the kidneys, and less than 5% via the bile duct . Nevirapine is highly lipophilic at physiological pH and is rapidly and widely distributed throughout the body .
Result of Action
The result of Nevirapine’s action is the suppression of the viral load when used as initial antiretroviral therapy . It is generally only considered for use if the CD4 cell count is very low .
Action Environment
The efficacy and stability of Nevirapine can be influenced by various environmental factors. For instance, the presence of other antiretroviral drugs can enhance its effectiveness as part of a combination antiretroviral treatment . Severe hepatotoxicity and serious adverse cutaneous effects raise concerns about its safety . These side effects can be severe and should be checked for during the first few months of treatment .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Nevirapin hat eine Vielzahl von Anwendungen in der wissenschaftlichen Forschung, darunter:
Chemie: Wird als Modellverbindung für die Untersuchung von nicht-nukleosidischen Reverse-Transkriptase-Hemmern verwendet.
Biologie: Wird in der Forschung zur HIV-1-Replikation und zu Resistenzmechanismen eingesetzt.
Medizin: Bestandteil der antiretroviralen Therapie bei HIV-1-Infektionen. .
5. Wirkmechanismus
This compound übt seine Wirkung aus, indem es direkt an das Reverse-Transkriptase-Enzym von HIV-1 bindet. Diese Bindung führt zu einer Störung des katalytischen Zentrums des Enzyms und blockiert so die RNA-abhängige und DNA-abhängige DNA-Polymeraseaktivität. Diese Hemmung verhindert die Replikation von HIV-1 und reduziert die Viruslast im Körper des Patienten .
Ähnliche Verbindungen:
Efavirenz: Ein weiterer nicht-nukleosidischer Reverse-Transkriptase-Hemmer, der zur Behandlung von HIV-1 eingesetzt wird.
Etravirin: Bekannt für seine Wirksamkeit gegen HIV-1-Stämme, die gegenüber anderen nicht-nukleosidischen Reverse-Transkriptase-Hemmern resistent sind.
Rilpivirin: Ein neuerer nicht-nukleosidischer Reverse-Transkriptase-Hemmer mit einem günstigen Nebenwirkungsprofil
Eindeutigkeit von this compound: this compound ist einzigartig aufgrund seiner Fähigkeit, die Übertragung von HIV von Mutter zu Kind während der Geburt zu verhindern, ein Merkmal, das nicht häufig mit anderen nicht-nukleosidischen Reverse-Transkriptase-Hemmern verbunden ist. Darüber hinaus ermöglicht seine lange Halbwertszeit eine seltenerere Dosierung, was die Einhaltung der Behandlung durch den Patienten verbessern kann .
Biochemische Analyse
Biochemical Properties
Nevirapine is extensively biotransformed via cytochrome P450 3A4 metabolism to several hydroxylated metabolites . This interaction with the cytochrome P450 3A4 enzyme plays a crucial role in the biochemical reactions involving Nevirapine.
Cellular Effects
Nevirapine has been shown to be effective in reducing HIV-1 levels when used in combination with other antiretroviral agents . It influences cell function by inhibiting the action of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase, an enzyme crucial for the replication of the virus .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of Nevirapine involves its binding to HIV-1 reverse transcriptase . This binding inhibits the action of the enzyme, thereby preventing the replication of the virus at the molecular level .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
It is known that Nevirapine is extensively metabolized in the liver, primarily via cytochrome P450 3A4 .
Metabolic Pathways
Nevirapine is involved in the metabolic pathway of cytochrome P450 3A4 . It is extensively metabolized in the liver to several hydroxylated metabolites .
Transport and Distribution
The transport and distribution of Nevirapine within cells and tissues are complex processes that involve its extensive metabolism in the liver
Subcellular Localization
Given its role as an inhibitor of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase, it is likely to be localized where this enzyme is present within the cell .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions: Nevirapine can be synthesized through various methods, including the condensation of 2-chloro-3-cyanopyridine with cyclopropylamine, followed by cyclization and methylation. The reaction conditions typically involve the use of solvents like dimethylformamide and catalysts such as potassium carbonate .
Industrial Production Methods: Industrial production of nevirapine often involves large-scale synthesis using similar chemical routes but optimized for higher yields and purity. Techniques such as high-pressure homogenization and nanosuspension preparation are employed to enhance the solubility and bioavailability of the compound .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Arten von Reaktionen: Nevirapin unterliegt verschiedenen Arten von chemischen Reaktionen, darunter:
Oxidation: this compound kann oxidiert werden, um verschiedene Metaboliten zu bilden.
Reduktion: Reduktionsreaktionen sind seltener, können aber unter bestimmten Bedingungen auftreten.
Substitution: this compound kann Substitutionsreaktionen eingehen, insbesondere in Gegenwart von Nukleophilen
Häufige Reagenzien und Bedingungen:
Oxidation: Häufige Oxidationsmittel sind Wasserstoffperoxid und Kaliumpermanganat.
Reduktion: Reduktionsmittel wie Natriumborhydrid können verwendet werden.
Substitution: Nukleophile wie Amine und Thiole werden häufig in Substitutionsreaktionen eingesetzt
Hauptprodukte: Zu den Hauptprodukten, die aus diesen Reaktionen gebildet werden, gehören verschiedene Metaboliten und Derivate von this compound, die unterschiedliche pharmakologische Eigenschaften haben können .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Efavirenz: Another non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor used in the treatment of HIV-1.
Etravirine: Known for its efficacy against HIV-1 strains resistant to other non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors.
Rilpivirine: A newer non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor with a favorable side effect profile
Uniqueness of Nevirapine: Nevirapine is unique due to its ability to prevent mother-to-child transmission of HIV during childbirth, a feature not commonly associated with other non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Additionally, its long half-life allows for less frequent dosing, which can improve patient adherence to the treatment regimen .
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
2-cyclopropyl-7-methyl-2,4,9,15-tetrazatricyclo[9.4.0.03,8]pentadeca-1(11),3,5,7,12,14-hexaen-10-one | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C15H14N4O/c1-9-6-8-17-14-12(9)18-15(20)11-3-2-7-16-13(11)19(14)10-4-5-10/h2-3,6-8,10H,4-5H2,1H3,(H,18,20) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
NQDJXKOVJZTUJA-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC1=C2C(=NC=C1)N(C3=C(C=CC=N3)C(=O)N2)C4CC4 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C15H14N4O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID7031797 | |
| Record name | Nevirapine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID7031797 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
266.30 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Nevirapine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014383 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
>39.9 [ug/mL] (The mean of the results at pH 7.4), In water, 100 mg/l @ neutral pH, 1.05e-01 g/L | |
| Record name | SID865943 | |
| Source | Burnham Center for Chemical Genomics | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioassay/1996#section=Data-Table | |
| Description | Aqueous solubility in buffer at pH 7.4 | |
| Record name | Nevirapine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00238 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | NEVIRAPINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7164 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Nevirapine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014383 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Vapor Pressure |
3.4X10-9 mm Hg @ 25 °C /Estimated/ | |
| Record name | NEVIRAPINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7164 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Nevirapine binds directly to reverse transcriptase (RT) and blocks the RNA-dependent and DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activities by causing a disruption of the enzyme's catalytic site. The activity of nevirapine does not compete with template or nucleoside triphosphates., The binding site for nevirapine on HIV-1 reverse transcriptase is near, but not at the proposed site of active polymerization, in a deep pocket lying between the beta sheets of the palm and at the base of the thumb subdomains of the enzyme's p66 subunit. In the absence of nevirapine, the binding of deoxynucleoside triphosphate to the reverse transcriptase-template complex results in a change in the conformation of reverse transcriptase. This conformational change is followed by a magnesium-dependent chemical reaction in which deoxynucleoside triphosphate is incorporated into the newly forming viral DNA; the conformational change appears to be the rate-limiting step of the reverse transcriptase catalysis of viral DNA formation. Nevirapine appears to have no appreciable effect on the rate of or equilibrium constant for the conformational change but may slow the chemical reaction, which then becomes the rate-limiting step in the catalytic sequence. When nevirapine binds to the reverse transcriptase-template complex, changes may occur in the position of aspartic acid carboxyl groups in reverse transcriptase so that magnesium ions are not in proper alignment for the chemical reaction to occur efficiently, and the reaction is slowed. Therefore, although the nevirapine-reverse transcriptase-template complex may continue to bind deoxynucleoside triphosphate and to catalyze its incorporation into the newly forming viral DNA, it appears to do so at a slower rate., The mechanism of action of nevirapine differs from that of nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (e.g., abacavir, didanosine, lamivudine, stavudine, zalcitabine, zidovudine). Nucleoside antiretroviral agents require intracellular conversion to triphosphate metabolites, which then compete with naturally occurring deoxynucleoside triphosphates for incorporation into viral DNA by reverse transcriptase and cause premature viral DNA chain termination by preventing further 5 to 3 phosphodiester linkages. Nevirapine, however, is noncompetitive with respect to primer-template or nucleoside triphosphate binding and is specific for HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. The drug binds directly to heterodimeric HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and appears to inhibit viral RNA- and DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activities by disrupting the catalytic site of the enzyme., Nevirapine diffuses into the cell and binds to reverse transcriptase adjacent to the catalytic site. This induces conformational changes that inactivate the enzyme. Resistance develops rapidly in cells exposed to nevirapine. High-level resistance is associated with mutations at reverse transcriptase codons 101, 103, 106,108, 135, 181, 188, and 190. A single mutation at either codon 103 or 181 decreases susceptibility more than 100 fold. Cross-resistance may extend to all FDA-approved nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, especially with the codon 103 mutation., Nevirapine is a highly specific inhibitor of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase, and results of in vitro studies indicate that nevirapine does not appear to inhibit cellular DNA polymerases, including human alpha-, beta-, Gamma-, or Delta-polymerases. | |
| Record name | Nevirapine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00238 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | NEVIRAPINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7164 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
Crystals from pyridine and water | |
CAS No. |
129618-40-2 | |
| Record name | Nevirapine | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=129618-40-2 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Nevirapine [USAN:USP:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0129618402 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Nevirapine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00238 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | nevirapine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=759902 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | nevirapine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=641530 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Nevirapine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID7031797 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | NEVIRAPINE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/99DK7FVK1H | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | NEVIRAPINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7164 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Nevirapine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014383 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
247-249 °C, 196.06 °C | |
| Record name | Nevirapine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00238 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | NEVIRAPINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7164 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Nevirapine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014383 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details






Synthesis routes and methods III
Procedure details






Synthesis routes and methods IV
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods V
Procedure details




Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.
![3-((6-Chlorothiazolo[5,4-b]pyridin-2-yl)methoxy)-2,6-difluorobenzamide](/img/structure/B1678574.png)
![14-[2-(Diethylamino)ethyl]-10-[2-(2-hydroxyethylamino)ethylamino]-8-thia-14,15-diazatetracyclo[7.6.1.02,7.013,16]hexadeca-1(15),2(7),3,5,9,11,13(16)-heptaen-4-ol](/img/structure/B1678588.png)
