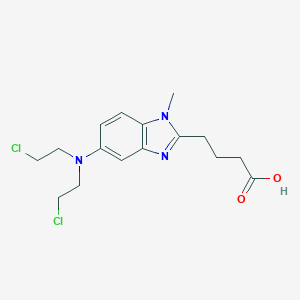
Bendamustine
Descripción general
Descripción
La bendamustina es un medicamento de quimioterapia que se usa principalmente en el tratamiento de la leucemia linfocítica crónica, el mieloma múltiple y el linfoma no Hodgkin . Pertenece a la clase de agentes alquilantes y funciona interfiriendo con la función del ADN y el ARN, lo que lleva a la muerte celular . La bendamustina se sintetizó por primera vez a principios de la década de 1960 en la República Democrática Alemana y se aprobó para su uso médico en los Estados Unidos en 2008 .
Métodos De Preparación
Rutas sintéticas y condiciones de reacción: El clorhidrato de bendamustina se puede sintetizar mediante un proceso de varios pasos. El intermedio clave, 1-metil-5-[bis(2-cloroetil)amino]-1H-benzimidazol-2-il]litio butanoato, se prepara y luego se convierte en clorhidrato de bendamustina . El proceso implica el uso de varios reactivos y disolventes, incluidos el ácido trifluoroacético y el acetonitrilo .
Métodos de producción industrial: La producción industrial de clorhidrato de bendamustina tiene como objetivo una alta pureza (≥99%) e implica pasos como la cromatografía líquida de alta resolución (HPLC) para la purificación . El proceso está diseñado para ser económico y respetuoso con el medio ambiente, evitando el uso de productos químicos peligrosos .
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
Tipos de reacciones: La bendamustina experimenta varios tipos de reacciones químicas, incluidas la alquilación, la hidrólisis y la oxidación . Como agente alquilante, forma enlaces cruzados intra e intercatenarios entre las bases del ADN, lo que lleva a la muerte celular .
Reactivos y condiciones comunes:
Alquilación: La bendamustina forma grupos alquilo electrófilos que se unen covalentemente a las bases del ADN.
Hidrólisis: El compuesto se hidroliza a metabolitos inactivos en el hígado.
Productos principales: Los productos principales formados a partir de estas reacciones incluyen los metabolitos inactivos y el ADN entrecruzado .
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
La bendamustina tiene una amplia gama de aplicaciones de investigación científica:
Mecanismo De Acción
La bendamustina ejerce sus efectos a través de múltiples mecanismos:
Alquilación: Forma enlaces cruzados intra e intercatenarios entre las bases del ADN, lo que lleva a la muerte celular.
Activación de respuestas al daño del ADN: La bendamustina activa las respuestas al estrés por daño del ADN y la apoptosis.
Inhibición de los puntos de control mitóticos: Inhibe los puntos de control mitóticos e induce la catástrofe mitótica.
Objetivos moleculares: Los principales objetivos son las bases del ADN, lo que lleva a la interrupción de la replicación y transcripción del ADN.
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
La bendamustina es única debido a su naturaleza bifuncional, combinando propiedades de los agentes alquilantes y los análogos de purina . Los compuestos similares incluyen:
Ciclofosfamida: Otro agente alquilante utilizado en quimioterapia.
Melfalán: Un agente alquilante utilizado para el mieloma múltiple.
Clorambucil: Utilizado para la leucemia linfocítica crónica.
En comparación con estos compuestos, la bendamustina ha mostrado una mayor estabilidad y un rango más amplio de actividad contra células quiescentes y en división .
Propiedades
IUPAC Name |
4-[5-[bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]-1-methylbenzimidazol-2-yl]butanoic acid | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C16H21Cl2N3O2/c1-20-14-6-5-12(21(9-7-17)10-8-18)11-13(14)19-15(20)3-2-4-16(22)23/h5-6,11H,2-4,7-10H2,1H3,(H,22,23) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
YTKUWDBFDASYHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CN1C2=C(C=C(C=C2)N(CCCl)CCCl)N=C1CCCC(=O)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C16H21Cl2N3O2 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
3543-75-7 (hydrochloride) | |
| Record name | Bendamustine [INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0016506277 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID2046888 | |
| Record name | Bendamustine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID2046888 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
358.3 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Bendamustine is a bifunctional mechlorethamine derivative capable of forming electrophilic alkyl groups that covalently bond to other molecules. Through this function as an alkylating agent, bendamustine causes intra- and inter-strand crosslinks between DNA bases resulting in cell death. It is active against both active and quiescent cells, although the exact mechanism of action is unknown., Multiple myeloma is a fatal hematological disease caused by malignant transformation of plasma cells. Bendamustine has been proven to be a potent alternative to melphalan in phase 3 studies, yet its molecular mode of action is still poorly understood. The four-myeloma cell lines NCI-H929, OPM-2, RPMI-8226, and U266 were cultured in vitro. Apoptosis was measured by flow cytometry after annexin V FITC and propidium iodide staining. Cell cycle distribution of cells was determined by DNA staining with propidium iodide. Intracellular levels of (phosphorylated) proteins were determined by western blot. /It was shown/ that bendamustine induces apoptosis with an IC50 of 35-65 mug/ml and with cleavage of caspase 3. Incubation with 10-30 mug/ml results in G2 cell cycle arrest in all four-cell lines. The primary DNA-damage signaling kinases ATM and Chk2, but not ATR and Chk1, are activated. The Chk2 substrate Cdc25A phosphatase is degraded and Cdc2 is inhibited by inhibitory phosphorylation of Tyr15 accompanied by increased cyclin B levels. Additionally, p53 activation occurs as phosphorylation of Ser15, the phosphorylation site for ATM. p53 promotes Cdc2 inhibition by upregulation of p21. Targeting of p38 MAPK by the selective inhibitor SB202190 significantly increases bendamustine induced apoptosis. Additionally, SB202190 completely abrogates G2 cell cycle arrest. Bendamustine induces ATM-Chk2-Cdc2-mediated G2 arrest and p53 mediated apoptosis. Inhibition of p38 MAPK augments apoptosis and abrogates G2 arrest and can be considered as a new therapeutic strategy in combination with bendamustine., Microarray-based gene expression profiling, real-time PCR, immunoblot, cell cycle, and functional DNA damage repair analyses were used to characterize response to bendamustine and compare it with chlorambucil and phosphoramide mustard. Bendamustine displays a distinct pattern of activity unrelated to other DNA-alkylating agents. Its mechanisms of action include activation of DNA-damage stress response and apoptosis, inhibition of mitotic checkpoints, and induction of mitotic catastrophe. In addition, unlike other alkylators, bendamustine activates a base excision DNA repair pathway rather than an alkyltransferase DNA repair mechanism. These results suggest that bendamustine possesses mechanistic features that differentiate it from other alkylating agents and may contribute to its distinct clinical efficacy profile., Bendamustine is a bifunctional mechlorethamine derivative containing a purine-like benzimidazole ring. Mechlorethamine and its derivatives form electrophilic alkyl groups. These groups form covalent bonds with electron-rich nucleophilic moieties, resulting in interstrand DNA crosslinks. The bifunctional covalent linkage can lead to cell death via several pathways. Bendamustine is active against both quiescent and dividing cells. The exact mechanism of action of bendamustine remains unknown. | |
| Record name | Bendamustine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB06769 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Bendamustine | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7763 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
CAS No. |
16506-27-7 | |
| Record name | Bendamustine | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=16506-27-7 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Bendamustine [INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0016506277 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Bendamustine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB06769 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Bendamustine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID2046888 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | 16506-27-7 | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | BENDAMUSTINE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/9266D9P3PQ | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Bendamustine | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7763 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.


![2-[Bis(2-ethylhexyl)amino]ethanol](/img/structure/B91584.png)
![1,4-Dimethylbenzo[a]pyrene](/img/structure/B91590.png)
