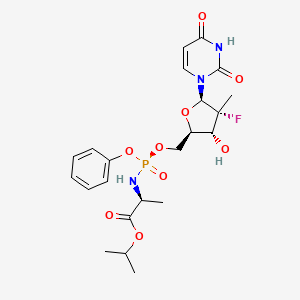
Sofosbuvir
- Cliquez sur DEMANDE RAPIDE pour recevoir un devis de notre équipe d'experts.
- Avec des produits de qualité à un prix COMPÉTITIF, vous pouvez vous concentrer davantage sur votre recherche.
Vue d'ensemble
Description
Sofosbuvir est un médicament antiviral à action directe utilisé pour traiter les infections chroniques par le virus de l’hépatite C (VHC). Il appartient à la famille des médicaments analogues nucléotidiques et agit en inhibant la polymérase ARN dépendante de l’ARN NS5B du VHC, qui est essentielle à la réplication virale . This compound a été découvert en 2007 et approuvé pour un usage médical aux États-Unis en 2013 . Il est commercialisé sous le nom de marque Sovaldi et figure sur la Liste des médicaments essentiels de l’Organisation mondiale de la santé .
Applications De Recherche Scientifique
Sofosbuvir has several scientific research applications, including:
Chemistry: This compound is used as a model compound in the study of nucleotide analogs and their synthesis.
Medicine: this compound is primarily used in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C infections.
Industry: This compound’s synthesis and production methods are studied to improve industrial-scale manufacturing processes and reduce production costs
Mécanisme D'action
Le sofosbuvir est un promédicament qui est métabolisé en sa forme active, le GS-461203, dans l’organisme . Cette forme active inhibe la polymérase ARN dépendante de l’ARN NS5B du VHC en agissant comme un substrat défectueux, ce qui met fin à la chaîne d’ARN viral et empêche la réplication . L’inhibition de cette enzyme est cruciale pour la suppression de la réplication du VHC et l’obtention d’une réponse virologique durable .
Méthodes De Préparation
La synthèse du sofosbuvir implique plusieurs étapes, notamment la préparation d’intermédiaires clés et la réaction de couplage finale. L’une des voies de synthèse implique l’utilisation de la (2’R)-2’-désoxy-2’-fluoro-2’-méthyluridine comme matière de départ. Ce composé est mis en réaction avec d’autres matières premières dans un solvant organique en présence d’un acide de Lewis et d’une base pour produire du this compound . Les conditions réactionnelles sont douces, et le procédé est adapté à la production industrielle à grande échelle .
Une autre méthode implique une préparation plus stéréosélective, qui permet de produire l’isomère souhaité sans avoir besoin d’une séparation intermédiaire. Cette méthode réduit les coûts de production et convient également à la production industrialisée .
Analyse Des Réactions Chimiques
Le sofosbuvir subit diverses réactions chimiques, notamment :
Oxydation : Le this compound peut être oxydé pour former son métabolite actif, le GS-461203, qui est un triphosphate.
Réduction : Les réactions de réduction ne sont généralement pas associées au this compound.
Substitution : Le this compound peut subir des réactions de substitution, en particulier impliquant l’atome de fluor sur le cycle furanose.
Les réactifs et les conditions usuels utilisés dans ces réactions comprennent des solvants organiques, des acides de Lewis et des bases . Les principaux produits formés à partir de ces réactions comprennent la forme triphosphate active du this compound et d’autres intermédiaires utilisés dans sa synthèse .
Applications de la recherche scientifique
Le this compound a plusieurs applications dans la recherche scientifique, notamment :
Médecine : Le this compound est principalement utilisé dans le traitement des infections chroniques par le virus de l’hépatite C.
Industrie : Les méthodes de synthèse et de production du this compound sont étudiées pour améliorer les procédés de fabrication à l’échelle industrielle et réduire les coûts de production
Comparaison Avec Des Composés Similaires
Le sofosbuvir est souvent comparé à d’autres agents antiviraux à action directe, tels que :
Ledipasvir : Utilisé en association avec le this compound pour le traitement du VHC.
Velpatasvir : Un autre agent antiviral utilisé en association avec le this compound pour un traitement pangénotypique du VHC.
Daclatasvir : Utilisé en association avec le this compound pour le traitement du VHC.
Simeprevir : Utilisé en association avec le this compound pour le traitement du VHC.
Remdesivir : Un agent antiviral utilisé pour le traitement de la COVID-19, qui cible également la polymérase ARN dépendante de l’ARN.
Le this compound est unique par sa forte barrière au développement de résistance et son efficacité contre plusieurs génotypes du VHC . Son association avec d’autres agents antiviraux améliore son efficacité et élargit son application dans le traitement de divers génotypes du VHC .
Propriétés
| Sofosbuvir is a direct-acting antiviral agent (pan-genotypic polymerase inhibitor) against the hepatitis C virus. HCV RNA replication is mediated by a membrane-associated multiprotein replication complex. The HCV polymerase (NS5B protein) is an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). It is the essential initiating and catalytic subunit of this replication complex and is critical for the viral replication cycle. There is no human homolog for HCV NS5B RdRp. Sofosbuvir is a monophosphorylated pyrimidine nucleotide prodrug that undergoes intracellular metabolism to form the pharmacologically active uridine analog triphosphate (GS-461203). GS-461203 competes with natural nucleotides for incorporation (by HCV NS5B) into the nascent RNA strand during replication of the viral genome. GS-461203 differs from endogenous pyrimidine nucleotides in that it has been modified at the 2' position with the addition of a methyl and a fluoro functional group. Incorporation of GS-461203 into nascent RNA strongly reduces the efficiency of further RNA elongation by RdRp, resulting in premature termination of RNA synthesis. The stopping of viral replication leads to a rapid decline of HCV viral load and clearing of HCV levels in the body. | |
Numéro CAS |
1190307-88-0 |
Formule moléculaire |
C22H29FN3O9P |
Poids moléculaire |
529.5 g/mol |
Nom IUPAC |
propan-2-yl 2-[[[(4R)-5-(2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)-4-fluoro-3-hydroxy-4-methyloxolan-2-yl]methoxy-phenoxyphosphoryl]amino]propanoate |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C22H29FN3O9P/c1-13(2)33-19(29)14(3)25-36(31,35-15-8-6-5-7-9-15)32-12-16-18(28)22(4,23)20(34-16)26-11-10-17(27)24-21(26)30/h5-11,13-14,16,18,20,28H,12H2,1-4H3,(H,25,31)(H,24,27,30)/t14?,16?,18?,20?,22-,36+/m1/s1 |
Clé InChI |
TTZHDVOVKQGIBA-IECBXEDQSA-N |
SMILES |
CC(C)OC(=O)C(C)NP(=O)(OCC1C(C(C(O1)N2C=CC(=O)NC2=O)(C)F)O)OC3=CC=CC=C3 |
SMILES isomérique |
CC(C)OC(=O)C(C)N[P@](=O)(OCC1C([C@@](C(O1)N2C=CC(=O)NC2=O)(C)F)O)OC3=CC=CC=C3 |
SMILES canonique |
CC(C)OC(=O)C(C)NP(=O)(OCC1C(C(C(O1)N2C=CC(=O)NC2=O)(C)F)O)OC3=CC=CC=C3 |
Apparence |
white solid powder |
Color/Form |
White to off-white crystalline solid |
Pureté |
>98% (or refer to the Certificate of Analysis) |
Durée de conservation |
>2 years if stored properly |
Solubilité |
Slightly soluble in water |
Stockage |
Dry, dark and at 0 - 4 C for short term (days to weeks) or -20 C for long term (months to years). |
Synonymes |
PSI-7977; PSI 7977; PSI7977; GS7977; GS-7977; GS 7977; Sofosbuvir; Sovaldi; Virunon; Vosevi; Hepcinat; Hepcvir; Resof; |
Origine du produit |
United States |
Q1: What is the mechanism of action of Sofosbuvir?
A1: this compound is a pan-genotypic inhibitor of the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) NS5B RNA polymerase, a key enzyme responsible for viral replication. [, , , , , ] It acts as a chain-terminating nucleotide analogue, interfering directly with the HCV life cycle by suppressing viral replication. [, , ]
Q2: How does this compound affect HCV after binding to NS5B polymerase?
A2: Upon entering hepatocytes (liver cells), this compound is metabolized into its active form, a nucleoside triphosphate. This active metabolite competes with naturally occurring nucleotides, ultimately leading to the termination of RNA chain elongation during HCV replication. [, ]
Q3: What is the molecular formula and weight of this compound?
A3: The scientific literature provided does not specify the exact molecular formula and weight of this compound.
Q4: How stable is this compound under various storage conditions?
A5: While specific stability data is limited in the provided research, this compound has been successfully formulated into tablets for oral administration. [, , , , , ] Stability indicating HPTLC methods have been developed for this compound and Daclatasvir in combination, highlighting the need for validated methods to assess drug stability. []
Q5: Does this compound have any catalytic properties?
A5: this compound itself doesn't possess catalytic properties. Its antiviral action stems from inhibiting the catalytic activity of the HCV NS5B polymerase.
Q6: Have any computational studies been conducted on this compound?
A6: There is no mention of specific computational chemistry studies on this compound within the provided research articles.
Q7: What formulation strategies have been explored for this compound?
A9: this compound is primarily formulated as tablets for oral administration. [, , , , , ] Further research exploring strategies to optimize this compound formulation for improved stability, solubility, and bioavailability is warranted.
Q8: Is there information regarding this compound's SHE compliance?
A8: The provided scientific research focuses primarily on the clinical efficacy and safety of this compound. Information regarding specific SHE (Safety, Health, and Environment) regulations and compliance is not discussed.
Q9: What is known about the pharmacokinetic profile of this compound?
A11: this compound is readily absorbed after oral administration, achieving peak plasma concentrations in approximately 30 minutes. [, ] It undergoes extensive hepatic metabolism, primarily by phosphorylation, into its active triphosphate form. [, , ] The primary metabolite, GS-331007, is largely inactive against HCV and is eliminated in the urine. []
Q10: What cell-based assays have been used to evaluate this compound's activity?
A13: this compound's antiviral activity has been extensively studied in cell culture using HCV replicons. [, , ] These replicons are engineered systems that allow for the replication of the HCV genome in cultured cells, enabling the assessment of antiviral activity. Resistance selection experiments have also been conducted in cell culture to understand the emergence of resistance to this compound. []
Q11: What is the efficacy of this compound in clinical trials?
A14: Clinical trials have demonstrated that this compound-based regimens achieve high sustained virological response (SVR) rates, signifying viral eradication, across various HCV genotypes and patient populations. [, , , , , , , , , , , , , , ] Notably, this compound-containing regimens have shown efficacy in treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced patients, as well as in those with cirrhosis. [, , , , , , , , , , , , , , ]
Q12: What are the primary mechanisms of resistance to this compound?
A15: The primary mechanism of this compound resistance involves mutations in the NS5B polymerase, specifically the S282T substitution. This mutation has been identified across all HCV genotypes and confers reduced susceptibility to this compound. [, , ]
Q13: Does cross-resistance occur between this compound and other antivirals?
A16: While S282T is the primary resistance mutation, other substitutions in NS5B can emerge during this compound treatment, and their impact on resistance and cross-resistance with other antivirals requires further investigation. [] Clinical studies have shown that this compound-containing regimens, particularly this compound/Velpatasvir/Voxilaprevir, are effective as salvage therapies in patients who have failed prior DAA treatments. []
Q14: Are there any specific drug delivery strategies for this compound?
A17: The provided research primarily focuses on the oral formulation and efficacy of this compound. [, , , , , ] Specific drug delivery and targeting strategies for this compound are not discussed in detail within these articles.
Q15: Are there any biomarkers associated with this compound treatment response?
A18: The research primarily focuses on sustained virologic response (SVR) as the primary indicator of this compound treatment efficacy. [, , , , , , , , , , , , , , ] The research does not delve into specific biomarkers to predict treatment response or identify potential adverse effects.
Q16: What analytical methods are used to quantify this compound?
A19: Several analytical techniques have been employed for this compound quantification, including high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and UV spectrophotometry. [, , , , , ] Stability indicating HPTLC methods have also been developed to assess this compound stability. []
Q17: Are there specific methods for analyzing this compound in biological samples?
A17: The provided research does not delve into specific details regarding the analysis of this compound in biological samples.
Q18: What is the environmental impact of this compound?
A18: The provided research focuses on the clinical aspects of this compound, and information regarding its environmental impact and degradation is not discussed.
Q19: What quality control measures are in place for this compound manufacturing?
A19: Specific quality control and assurance measures implemented during this compound development, manufacturing, and distribution are not discussed in detail in the provided research.
Q20: Does this compound elicit any immune responses?
A20: The provided scientific literature primarily focuses on the antiviral efficacy and safety profile of this compound. Information concerning its potential immunogenicity and effects on immunological responses is not discussed.
Q21: Does this compound interact with drug transporters?
A26: Preliminary research suggests that genetic variants in drug transporter genes like ABCB1 might affect this compound's primary metabolite concentration. [] This highlights the need for further investigation into potential drug-transporter interactions.
Q22: Does this compound affect drug-metabolizing enzymes?
A22: The provided research focuses on this compound's interaction with HCV and its clinical efficacy. It doesn't detail its impact on drug-metabolizing enzyme activity.
Q23: What is known about the biocompatibility of this compound?
A23: The primary focus of the research is this compound's clinical effectiveness and safety in treating HCV. Specific details regarding its biocompatibility and biodegradability are not discussed.
Q24: Are there any alternative therapies to this compound-based regimens for HCV?
A29: The landscape of HCV treatment has evolved significantly with the advent of direct-acting antivirals (DAAs). [, , , , , , ] Prior to DAAs, the standard of care involved interferon-based therapies, which were associated with significant side effects and lower efficacy. [, , , , , ] this compound, as a highly effective DAA, has largely replaced interferon-based therapies as the preferred treatment option for most patients.
Q25: Are there strategies for recycling or managing this compound waste?
A25: The research provided does not offer information on this compound waste management or recycling strategies.
Q26: What research tools and resources have been crucial in this compound research?
A26: While not explicitly stated, the research highlights the use of several key tools and resources, including:
- HCV replicons: Essential for evaluating this compound's antiviral activity and resistance profiling. [, , ]
- Clinical trial networks: Collaborative efforts across multiple research centers were crucial for conducting large-scale clinical trials. [, , , , , , , , , , , , , , ]
- Analytical techniques: Methods like HPLC and UV spectrophotometry are vital for this compound quantification and stability studies. [, , , , , ]
Q27: What were the major milestones in the development of this compound?
A27: Key milestones in this compound's development include:
- Clinical trials: Successful completion of Phase 2 and 3 clinical trials demonstrating high SVR rates across HCV genotypes. [, , , , , , , , , , , , , , ]
- Regulatory approval: FDA approval of this compound in 2013, marking a significant advancement in HCV treatment. [, ]
- Real-world effectiveness: Continued evaluation of this compound's efficacy and safety in broader patient populations. [, ]
Q28: How has this compound research fostered cross-disciplinary collaborations?
A28: The development of this compound has spurred collaborations across various scientific disciplines, including:
- Virology and Molecular Biology: Understanding HCV replication mechanisms and resistance pathways. [, , ]
- Medicinal Chemistry and Pharmacology: Designing, synthesizing, and evaluating the drug's pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties. [, , , , ]
- Clinical Medicine and Hepatology: Conducting clinical trials, evaluating efficacy and safety, and managing HCV-infected patients. [, , , , , , , , , , , , , , ]
- Analytical Chemistry: Developing and validating methods for this compound quantification and quality control. [, , , , , ]
Avertissement et informations sur les produits de recherche in vitro
Veuillez noter que tous les articles et informations sur les produits présentés sur BenchChem sont destinés uniquement à des fins informatives. Les produits disponibles à l'achat sur BenchChem sont spécifiquement conçus pour des études in vitro, qui sont réalisées en dehors des organismes vivants. Les études in vitro, dérivées du terme latin "in verre", impliquent des expériences réalisées dans des environnements de laboratoire contrôlés à l'aide de cellules ou de tissus. Il est important de noter que ces produits ne sont pas classés comme médicaments et n'ont pas reçu l'approbation de la FDA pour la prévention, le traitement ou la guérison de toute condition médicale, affection ou maladie. Nous devons souligner que toute forme d'introduction corporelle de ces produits chez les humains ou les animaux est strictement interdite par la loi. Il est essentiel de respecter ces directives pour assurer la conformité aux normes légales et éthiques en matière de recherche et d'expérimentation.



![N-[4-(2-Benzimidazolyl)phenyl]maleimide](/img/structure/B1194385.png)