Chlorhydrate de saxagliptine
Vue d'ensemble
Description
Le Saxagliptin Hydrochlorure est un médicament hypoglycémiant à administration orale utilisé dans la prise en charge du diabète de type 2. Il appartient à la classe des inhibiteurs de la dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4), qui agissent en augmentant les niveaux d'hormones incrétines dans l'organisme. Ces hormones aident à réguler la glycémie en augmentant la production d'insuline et en diminuant la production de glucose par le foie .
Applications De Recherche Scientifique
Saxagliptin Hydrochloride has a wide range of scientific research applications:
Chemistry: It is used in the study of enzyme inhibitors and their effects on metabolic pathways.
Biology: It is used to understand the role of incretin hormones in glucose regulation.
Medicine: It is primarily used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus to improve glycemic control.
Industry: It is used in the pharmaceutical industry for the production of antidiabetic medications
Analyse Biochimique
Biochemical Properties
Saxagliptin hydrochloride plays a crucial role in biochemical reactions by inhibiting the DPP-4 enzyme. This inhibition prevents the degradation of incretin hormones such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). By maintaining higher levels of these hormones, saxagliptin hydrochloride enhances insulin secretion and decreases glucagon release, leading to improved glycemic control . The compound interacts with the DPP-4 enzyme by forming a reversible, histidine-assisted covalent bond between its nitrile group and the serine residue in the active site of DPP-4 .
Cellular Effects
Saxagliptin hydrochloride influences various cellular processes, particularly in pancreatic beta cells. By inhibiting DPP-4, it increases the levels of GLP-1 and GIP, which in turn stimulate insulin secretion from beta cells. This leads to improved glucose uptake and utilization by cells, thereby lowering blood glucose levels . Additionally, saxagliptin hydrochloride has been shown to have minimal effects on cell signaling pathways and gene expression, making it a relatively safe option for long-term use .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of saxagliptin hydrochloride involves the inhibition of the DPP-4 enzyme. This enzyme is responsible for the degradation of incretin hormones. By inhibiting DPP-4, saxagliptin hydrochloride increases the half-life of GLP-1 and GIP, enhancing their biological effects . The compound forms a reversible covalent bond with the active site of DPP-4, which prevents the enzyme from degrading incretin hormones .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, the effects of saxagliptin hydrochloride have been observed over various time periods. The compound is stable and maintains its inhibitory effects on DPP-4 for up to 24 hours post-administration . Long-term studies have shown that saxagliptin hydrochloride remains effective in improving glycemic control without significant degradation or loss of potency .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In animal models, the effects of saxagliptin hydrochloride vary with different dosages. At lower doses, the compound effectively inhibits DPP-4 and improves glycemic control without adverse effects . At higher doses, saxagliptin hydrochloride may cause toxic effects, including gastrointestinal disturbances and potential hepatotoxicity . It is important to determine the optimal dosage to maximize therapeutic benefits while minimizing adverse effects.
Metabolic Pathways
Saxagliptin hydrochloride is primarily metabolized by the cytochrome P450 3A4/5 (CYP3A4/5) enzymes in the liver . The major metabolite, 5-hydroxy saxagliptin, retains some inhibitory activity against DPP-4 but is less potent than the parent compound . The metabolic pathways involve hydroxylation and subsequent conjugation reactions, leading to the formation of various metabolites that are excreted via urine and feces .
Transport and Distribution
Saxagliptin hydrochloride is well-absorbed and distributed throughout the body. It has a bioavailability of approximately 75% and reaches peak plasma concentrations within 2 hours of oral administration . The compound is primarily excreted through the urine, with a smaller portion eliminated via the bile . Saxagliptin hydrochloride does not significantly bind to plasma proteins, allowing for efficient distribution to target tissues .
Subcellular Localization
The subcellular localization of saxagliptin hydrochloride is primarily within the cytoplasm, where it interacts with the DPP-4 enzyme . The compound does not require specific targeting signals or post-translational modifications for its activity. Its inhibitory effects on DPP-4 are exerted directly within the cytoplasmic compartment, leading to increased levels of active incretin hormones .
Méthodes De Préparation
Voies de synthèse et conditions de réaction : La synthèse du Saxagliptin Hydrochlorure implique plusieurs étapes clés. Une méthode courante consiste à coupler deux dérivés d'acides aminés en présence d'un agent de couplage. Le couplage amido de (S)-(+)-p-toluènesulfonamide, d'éthoxyde de titane(IV) et d'adamantane-1-carboxaldéhyde pour obtenir de l'hydroxybenzotriazole et de l'EDC (1-éthyl-3-(3-diméthylaminopropyl)carbodiimide) est une étape cruciale .
Méthodes de production industrielle : La production industrielle du Saxagliptin Hydrochlorure implique souvent l'utilisation de la chromatographie liquide haute performance (HPLC) pour la quantification et la validation du composé. Cette méthode garantit la pureté et la qualité du produit final .
Analyse Des Réactions Chimiques
Types de réactions : Le Saxagliptin Hydrochlorure subit diverses réactions chimiques, notamment :
Oxydation : Cette réaction implique l'ajout d'oxygène ou l'élimination d'hydrogène.
Réduction : Cette réaction implique l'ajout d'hydrogène ou l'élimination d'oxygène.
Substitution : Cette réaction implique le remplacement d'un atome ou d'un groupe d'atomes par un autre.
Réactifs et conditions courantes : Les réactifs courants utilisés dans ces réactions comprennent des agents oxydants comme le permanganate de potassium, des agents réducteurs comme le borohydrure de sodium et des agents de substitution comme les halogènes. Les conditions de ces réactions impliquent généralement des températures et des niveaux de pH contrôlés pour garantir le résultat souhaité .
Principaux produits formés : Les principaux produits formés à partir de ces réactions comprennent divers intermédiaires qui sont essentiels à la synthèse du Saxagliptin Hydrochlorure. Ces intermédiaires sont ensuite traités pour obtenir le composé final .
4. Applications de recherche scientifique
Le Saxagliptin Hydrochlorure a une large gamme d'applications de recherche scientifique :
Chimie : Il est utilisé dans l'étude des inhibiteurs enzymatiques et de leurs effets sur les voies métaboliques.
Biologie : Il est utilisé pour comprendre le rôle des hormones incrétines dans la régulation du glucose.
Médecine : Il est principalement utilisé dans le traitement du diabète de type 2 pour améliorer le contrôle glycémique.
Industrie : Il est utilisé dans l'industrie pharmaceutique pour la production de médicaments antidiabétiques
5. Mécanisme d'action
Le Saxagliptin Hydrochlorure agit en inhibant l'enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4). Cette inhibition augmente les niveaux d'hormones incrétines telles que le peptide-1 semblable au glucagon (GLP-1) et le polypeptide insulinotrope dépendant du glucose (GIP). Ces hormones contribuent à abaisser la glycémie en augmentant la sécrétion d'insuline et en diminuant la sécrétion de glucagon par le foie .
Composés similaires :
Métformine : Un autre médicament antidiabétique qui améliore la sensibilité à l'insuline.
Sémiglutide : Un agoniste du récepteur GLP-1 qui mime les effets des hormones incrétines.
Comparaison :
Saxagliptin Hydrochlorure vs. Métformine : Le Saxagliptin Hydrochlorure agit en inhibant la DPP-4, tandis que la metformine améliore la sensibilité à l'insuline.
Saxagliptin Hydrochlorure vs. Sémiglutide : Les deux médicaments augmentent les niveaux d'hormones incrétines, mais le sémiglutide est un agoniste du récepteur GLP-1, tandis que le Saxagliptin Hydrochlorure est un inhibiteur de la DPP-4.
Le Saxagliptin Hydrochlorure se distingue par son mécanisme d'action spécifique et son efficacité dans les thérapies combinées pour le diabète de type 2.
Mécanisme D'action
Saxagliptin Hydrochloride works by inhibiting the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4). This inhibition increases the levels of incretin hormones such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). These hormones help lower blood sugar levels by increasing insulin secretion and decreasing glucagon secretion from the liver .
Comparaison Avec Des Composés Similaires
Metformin: Another antidiabetic drug that improves insulin sensitivity.
Semaglutide: A GLP-1 receptor agonist that mimics the effects of incretin hormones.
Comparison:
Saxagliptin Hydrochloride vs. Metformin: Saxagliptin Hydrochloride works by inhibiting DPP-4, while Metformin improves insulin sensitivity.
Saxagliptin Hydrochloride vs. Semaglutide: Both drugs increase the levels of incretin hormones, but Semaglutide is a GLP-1 receptor agonist, while Saxagliptin Hydrochloride is a DPP-4 inhibitor.
Saxagliptin Hydrochloride stands out due to its specific mechanism of action and its effectiveness in combination therapies for type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Propriétés
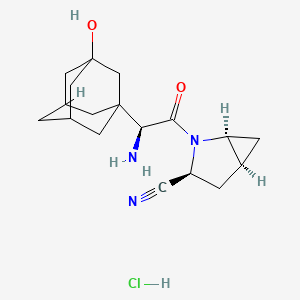
IUPAC Name |
(1S,3S,5S)-2-[(2S)-2-amino-2-(3-hydroxy-1-adamantyl)acetyl]-2-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-3-carbonitrile;hydrochloride | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C18H25N3O2.ClH/c19-8-13-2-12-3-14(12)21(13)16(22)15(20)17-4-10-1-11(5-17)7-18(23,6-10)9-17;/h10-15,23H,1-7,9,20H2;1H/t10?,11?,12-,13+,14+,15-,17?,18?;/m1./s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
TUAZNHHHYVBVBR-NHKADLRUSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1C2CC2N(C1C#N)C(=O)C(C34CC5CC(C3)CC(C5)(C4)O)N.Cl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C1[C@@H]2C[C@@H]2N([C@@H]1C#N)C(=O)[C@H](C34CC5CC(C3)CC(C5)(C4)O)N.Cl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C18H26ClN3O2 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID50991191 | |
| Record name | Saxagliptin hydrochloride | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID50991191 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
351.9 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
CAS No. |
709031-78-7 | |
| Record name | Saxagliptin hydrochloride | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0709031787 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Saxagliptin hydrochloride | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID50991191 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | (1S,3S,5S)-2-[(2S)-2-Amino-2-(3-hydroxyadamantan-1-yl)acetyl]-2-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-3-carbonitrile hydrochloride | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | SAXAGLIPTIN HYDROCHLORIDE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/Z8J84YIX6L | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
A: Saxagliptin Hydrochloride functions as a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor. [, , , ] This enzyme typically breaks down incretin hormones like glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). By inhibiting DPP-4, Saxagliptin Hydrochloride increases the levels of these incretin hormones. This, in turn, stimulates insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells and suppresses glucagon release, ultimately leading to improved glycemic control. [, , ]
A: Saxagliptin Hydrochloride is represented by the molecular formula C18H25N3O2·HCl. Its molecular weight is 351.87 g/mol. [, ]
A: Several spectroscopic methods prove valuable in the analysis of Saxagliptin Hydrochloride. These include: * X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD): This technique is used to identify different crystalline forms of Saxagliptin Hydrochloride, such as the dihydrate form. [, ] * Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR): FTIR aids in confirming the identity of Saxagliptin Hydrochloride and can also be used to study drug-excipient compatibility. [, , ] * UV-Vis Spectrophotometry: This technique is commonly employed for quantitative analysis of Saxagliptin Hydrochloride, often in conjunction with HPLC. [, , , , ]
A: Saxagliptin Hydrochloride exhibits instability due to a tendency for intra-molecular cyclization, forming a cyclicamidine. [] Careful selection of excipients during formulation is crucial to minimize this degradation pathway. [, ] Studies have shown compatibility with excipients like Methocel, Polyethylene Glycol (PEG), and various Opadry polymers. []
A: While the provided research does not offer a detailed SAR analysis, it is understood that even minor structural changes to Saxagliptin Hydrochloride could alter its binding affinity to DPP-4, thereby affecting its potency and selectivity. [, ] Further research in this area would be valuable.
A: The inherent instability of Saxagliptin Hydrochloride, particularly its susceptibility to cyclization, poses a significant formulation challenge. [, ] To enhance its stability and bioavailability, various strategies are employed, including the use of suitable excipients, controlled release formulations, and potentially, alternative routes of administration like buccal delivery. [, , , ]
A: Saxagliptin Hydrochloride undergoes significant hepatic metabolism. []
A: It possesses an elimination half-life of approximately 2.5 hours. [] This relatively short half-life necessitates regular dosing to maintain therapeutic levels.
A: Yes, research supports the efficacy of Saxagliptin Hydrochloride in managing Type 2 Diabetes. [, ] While specific details on preclinical models and clinical trials are not provided in the research excerpts, it is understood that the compound has been tested in both settings.
A: While the research excerpts do not specifically mention targeted delivery systems for Saxagliptin Hydrochloride, the development of buccal patches for this drug suggests exploration of alternative routes of administration. [] This could potentially enhance its bioavailability and efficacy. Further research on targeted delivery systems for this drug could be beneficial.
A: Several analytical techniques are employed for the quantification of Saxagliptin Hydrochloride.
* High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC): HPLC, often coupled with UV detection, is a widely used method for the separation and quantification of Saxagliptin Hydrochloride, both alone and in combination with other drugs like Metformin Hydrochloride and Dapagliflozin. [, , , , , , ] * UV-Vis Spectrophotometry: This technique, frequently used in conjunction with HPLC, provides a simple and rapid method for quantitative analysis. [, , , ] * High-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC): HPTLC offers a valuable alternative for analyzing Saxagliptin Hydrochloride in pharmaceutical preparations, especially in combination with other antidiabetic agents. []
A: The dissolution rate of Saxagliptin Hydrochloride is a critical factor influencing its bioavailability. [, ] Faster dissolution generally translates to better absorption and potentially higher efficacy. Formulation strategies often aim to enhance the dissolution rate of the drug. []
A: Analytical methods employed for Saxagliptin Hydrochloride analysis are rigorously validated according to ICH (International Conference on Harmonization) guidelines. [, , , ] Key validation parameters include: * Linearity: Assessing the method's ability to generate a linear response over a specific concentration range. * Accuracy: Determining how close the measured values are to the true value. * Precision: Evaluating the reproducibility of the method, often expressed as relative standard deviation. * Specificity: Confirming the method's ability to differentiate Saxagliptin Hydrochloride from other components in the sample. * Robustness: Examining the method's resilience to deliberate variations in analytical parameters.
A: The introduction of Saxagliptin Hydrochloride marked a significant advancement in Type 2 Diabetes treatment. [, ] As a highly selective DPP-4 inhibitor, it offered a novel mechanism for improving glycemic control with a generally favorable safety profile. Its development underscores the ongoing pursuit of more effective and well-tolerated therapies for this chronic condition.
Avertissement et informations sur les produits de recherche in vitro
Veuillez noter que tous les articles et informations sur les produits présentés sur BenchChem sont destinés uniquement à des fins informatives. Les produits disponibles à l'achat sur BenchChem sont spécifiquement conçus pour des études in vitro, qui sont réalisées en dehors des organismes vivants. Les études in vitro, dérivées du terme latin "in verre", impliquent des expériences réalisées dans des environnements de laboratoire contrôlés à l'aide de cellules ou de tissus. Il est important de noter que ces produits ne sont pas classés comme médicaments et n'ont pas reçu l'approbation de la FDA pour la prévention, le traitement ou la guérison de toute condition médicale, affection ou maladie. Nous devons souligner que toute forme d'introduction corporelle de ces produits chez les humains ou les animaux est strictement interdite par la loi. Il est essentiel de respecter ces directives pour assurer la conformité aux normes légales et éthiques en matière de recherche et d'expérimentation.



![3-(1H-indol-2-yl)-2-[[5-[2-(4-methylphenyl)ethynyl]thiophen-2-yl]sulfonylamino]propanoic acid](/img/structure/B610628.png)