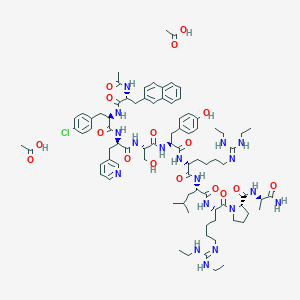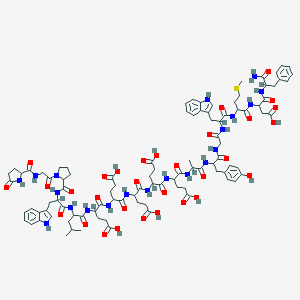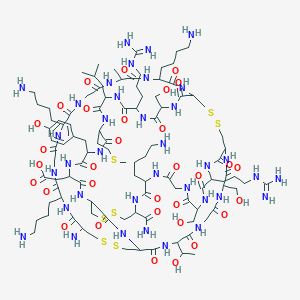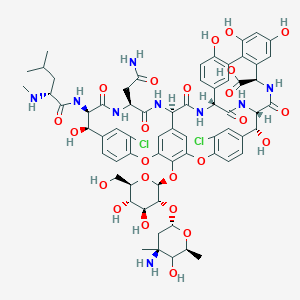
バンコマイシン
概要
説明
バンコマイシンは、メチシリン耐性黄色ブドウ球菌(MRSA)やクロストリジウム・ディフィシルなど、グラム陽性菌が原因の重篤な細菌感染症の治療に主に使用されるグリコペプチド系抗生物質です . 1956年にボルネオの土壌サンプルから初めて単離され、以来、抗生物質耐性感染症の対策に不可欠なツールとなっています .
2. 製法
バンコマイシンは、アミコラトプシス・オリエンタリス菌の発酵によって生成されます . 産業生産には、以下のいくつかのステップが含まれます。
発酵: アミコラトプシス・オリエンタリス菌を栄養豊富な培地で培養し、バンコマイシンを生成します。
抽出: 抗生物質を発酵液から有機溶媒を用いて抽出します。
3. 化学反応の分析
バンコマイシンは、以下のものを含むさまざまな化学反応を起こします。
酸化と還元: これらの反応は、バンコマイシン分子の官能基を変え、その活性を変化させる可能性があります。
置換反応: クロマトグラフィー法で使用されるアセトニトリルやメタノールなど、一般的な試薬があります.
主な生成物: 主な生成物は、抗生物質の性質を保持した精製バンコマイシンです.
作用機序
バンコマイシンは、細菌の細胞壁合成を阻害することで作用します。 細胞壁前駆体ユニットのD-アラニル-D-アラニン末端に結合し、細胞壁への組み込みを阻止するため、細菌の細胞壁を弱体化させ、細胞溶解と死滅を引き起こします . この機序により、グラム陽性菌に対して非常に有効となっています .
科学的研究の応用
バンコマイシンは、科学研究において幅広い用途があります。
生化学分析
Biochemical Properties
Vancomycin acts by binding to the D-alanyl-D-alanine moieties of the NAM/NAG-peptides, preventing the incorporation of these subunits into the peptidoglycan matrix, which forms the major structural component of Gram-positive bacterial cell walls . This interaction is non-covalent and results in the inhibition of cell wall synthesis . Vancomycin’s activity is concentration-independent, also referred to as “time-dependent,” and its clinical activity can be affected by factors such as variable tissue distribution, inoculum size, and emerging resistance .
Cellular Effects
Vancomycin primarily targets bacterial cells, where it disrupts cell wall synthesis, leading to cell death . It has been shown to have variable effects on different types of cells. For example, it has been found to reduce cell viability by 20% to 30% with increasing concentration up from 0.2 mg/mL . It also induces oxidative stress, as indicated by a reduction in the antioxidant activity of SOD2 and an increase in the MDA level .
Molecular Mechanism
Vancomycin exerts its effects at the molecular level by forming an intricate network of hydrogen bonds with the D-Ala-D-Ala region of Lipid II, interfering with the peptidoglycan layer maturation process . This binding prevents the incorporation of N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) and N-acetylglucosamine (NAG)-peptide subunits into the peptidoglycan matrix .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
The pharmacokinetic profile of vancomycin is complex and can be characterized by either a 2- or 3-compartment pharmacokinetic profile . In patients with normal creatinine clearance, vancomycin has an α-distribution phase of approximately 30 minutes to 1 hour and a β-elimination half-life of 6–12 hours . Over time, the effects of vancomycin can change due to factors such as the development of resistance .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In animal models, the effects of vancomycin can vary with different dosages. For instance, in beagle dogs, vancomycin is administered intravenously at a dose rate of 20 mg/kg over a 1-hour period at 12-hour intervals . The effects of vancomycin in animal models can also be influenced by factors such as the animal’s health status and the presence of other medications.
Metabolic Pathways
Vancomycin is not appreciably metabolized and is eliminated primarily via the renal route, with more than 80% to 90% recovered unchanged in urine within 24 hours after administration of a single dose . It has been suggested that vancomycin disrupts amino acids metabolism, fatty acids biosynthesis, energy metabolism, and lipid metabolism .
Transport and Distribution
Vancomycin is administered intravenously and has a volume of distribution of 0.4–1 L/kg . It penetrates into most body spaces, although the concentrations obtained are variable and somewhat dependent on the degree of inflammation present .
Subcellular Localization
Vancomycin accumulates in lysosomes of proximal tubular cells throughout 10 days of treatment . The subcellular localization of vancomycin in the renal cortices of rats was determined with ultrathin sections by immunogold labeling .
準備方法
Vancomycin is produced through the fermentation of the bacterium Amycolatopsis orientalis . The industrial production involves several steps:
Fermentation: Amycolatopsis orientalis is cultured in a nutrient-rich medium to produce vancomycin.
Extraction: The antibiotic is extracted from the fermentation broth using organic solvents.
Purification: High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is commonly used to purify vancomycin.
化学反応の分析
Vancomycin undergoes various chemical reactions, including:
Oxidation and Reduction: These reactions can modify the functional groups on the vancomycin molecule, potentially altering its activity.
Substitution Reactions: Common reagents include acetonitrile and methanol, used in chromatographic methods.
Major Products: The primary product is the purified vancomycin, which retains its antibiotic properties.
類似化合物との比較
バンコマイシンは、しばしば以下のような他の抗生物質と比較されます。
リネゾリド: タンパク質合成を阻害する合成オキサゾリジノン系抗生物質です.
ダプトマイシン: 細胞膜機能を破壊するリポペプチド系抗生物質です.
チゲサイクリン: タンパク質合成を阻害するグリシルサイクリン系抗生物質です.
テイコプラニン: 作用機序が類似している別のグリコペプチド系抗生物質です.
バンコマイシンのユニークな点は、抗生物質耐性菌が原因の重篤な感染症を治療できる点であり、現代医学において不可欠なツールとなっています .
特性
CAS番号 |
1404-90-6 |
|---|---|
分子式 |
C66H75Cl2N9O24 |
分子量 |
1449.2 g/mol |
IUPAC名 |
48-[3-[(4S)-4-amino-5-hydroxy-4,6-dimethyloxan-2-yl]oxy-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-22-(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)-5,15-dichloro-2,18,32,35,37-pentahydroxy-19-[[4-methyl-2-(methylamino)pentanoyl]amino]-20,23,26,42,44-pentaoxo-7,13-dioxa-21,24,27,41,43-pentazaoctacyclo[26.14.2.23,6.214,17.18,12.129,33.010,25.034,39]pentaconta-3,5,8(48),9,11,14,16,29(45),30,32,34(39),35,37,46,49-pentadecaene-40-carboxylic acid |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C66H75Cl2N9O24/c1-23(2)12-34(71-5)58(88)76-49-51(83)26-7-10-38(32(67)14-26)97-40-16-28-17-41(55(40)101-65-56(54(86)53(85)42(22-78)99-65)100-44-21-66(4,70)57(87)24(3)96-44)98-39-11-8-27(15-33(39)68)52(84)50-63(93)75-48(64(94)95)31-18-29(79)19-37(81)45(31)30-13-25(6-9-36(30)80)46(60(90)77-50)74-61(91)47(28)73-59(89)35(20-43(69)82)72-62(49)92/h6-11,13-19,23-24,34-35,42,44,46-54,56-57,65,71,78-81,83-87H,12,20-22,70H2,1-5H3,(H2,69,82)(H,72,92)(H,73,89)(H,74,91)(H,75,93)(H,76,88)(H,77,90)(H,94,95)/t24?,34?,35?,42?,44?,46?,47?,48?,49?,50?,51?,52?,53?,54?,56?,57?,65?,66-/m0/s1 |
InChIキー |
MYPYJXKWCTUITO-BSRCFTEOSA-N |
SMILES |
CC1C(C(CC(O1)OC2C(C(C(OC2OC3=C4C=C5C=C3OC6=C(C=C(C=C6)C(C(C(=O)NC(C(=O)NC5C(=O)NC7C8=CC(=C(C=C8)O)C9=C(C=C(C=C9O)O)C(NC(=O)C(C(C1=CC(=C(O4)C=C1)Cl)O)NC7=O)C(=O)O)CC(=O)N)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC)O)Cl)CO)O)O)(C)N)O |
異性体SMILES |
CC1C([C@@](CC(O1)OC2C(C(C(OC2OC3=C4C=C5C=C3OC6=C(C=C(C=C6)C(C(C(=O)NC(C(=O)NC5C(=O)NC7C8=CC(=C(C=C8)O)C9=C(C=C(C=C9O)O)C(NC(=O)C(C(C1=CC(=C(O4)C=C1)Cl)O)NC7=O)C(=O)O)CC(=O)N)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC)O)Cl)CO)O)O)(C)N)O |
正規SMILES |
CC1C(C(CC(O1)OC2C(C(C(OC2OC3=C4C=C5C=C3OC6=C(C=C(C=C6)C(C(C(=O)NC(C(=O)NC5C(=O)NC7C8=CC(=C(C=C8)O)C9=C(C=C(C=C9O)O)C(NC(=O)C(C(C1=CC(=C(O4)C=C1)Cl)O)NC7=O)C(=O)O)CC(=O)N)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC)O)Cl)CO)O)O)(C)N)O |
外観 |
White to off-white solid powder |
| Vancomycin is an antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections. It is a member of the glycopeptide antibiotic class and is effective mostly against Gram-positive bacteria. | |
沸点 |
N/A |
melting_point |
N/A |
| 1404-90-6 | |
物理的記述 |
Tan to brown solid; [HSDB] |
ピクトグラム |
Health Hazard |
純度 |
>98% (or refer to the Certificate of Analysis) |
関連するCAS |
1404-93-9 (hydrochloride) 64685-75-2 (sulfate) |
賞味期限 |
When reconstituted with sterile water for injection, vancomycin hydrochloride injection is stable for 2 weeks at room temperature; the manufacturers state that reconstituted injections may be stored for 96 hours at 2 - 8 °C without substantial loss of potency. When reconstituted as directed in 0.9% sodium chloride injection or 5% dextrose injection, solutions prepared from ADD-Vantage vials of the drug are stable for 24 hours at room temperature. Vancomycin solutions containing 5 mg/mL in 0.9% sodium chloride injection or 5% dextrose injection are reportedly stable for at least 17 days when stored at 24 °C in glass or PVC containers and for at least 63 days when stored at 5 °C or -10 °C in glass containers. Following reconstitution with sterile water for injection as directed, vancomycin solutions that have been further diluted to a concentration of 5 mg/mL in 5 - 30% dextrose injection are stable when stored in plastic syringes for 24 hours at 4 eg C and then subsequently for 2 hours at room temperature. Solutions are stable for two weeks at room temp or longer if refrigerated. /Hydrochloride/ |
溶解性 |
White solid; solubility in water: greater than 100 mg/mL; moderately soluble in methanol; insoluble in higher alcohols, acetone, ether; UV max absorption (water): 282 nm (e = 40, 1%, 1 cm) /Vancomycin hydrochloride/ |
ソース |
Synthetic |
同義語 |
AB-Vancomycin Diatracin Hydrochloride, Vancomycin Sulfate, Vancomycin Vanco Azupharma VANCO-cell Vanco-saar Vancocin Vancocin HCl Vancocine Vancomicina Abbott Vancomicina Chiesi Vancomicina Combino Phar Vancomicina Norman Vancomycin Vancomycin Hexal Vancomycin Hydrochloride Vancomycin Lilly Vancomycin Phosphate (1:2) Vancomycin Phosphate (1:2), Decahydrate Vancomycin Sulfate Vancomycin-ratiopharm Vancomycine Dakota |
製品の起源 |
United States |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
試験管内研究製品の免責事項と情報
BenchChemで提示されるすべての記事および製品情報は、情報提供を目的としています。BenchChemで購入可能な製品は、生体外研究のために特別に設計されています。生体外研究は、ラテン語の "in glass" に由来し、生物体の外で行われる実験を指します。これらの製品は医薬品または薬として分類されておらず、FDAから任何の医療状態、病気、または疾患の予防、治療、または治癒のために承認されていません。これらの製品を人間または動物に体内に導入する形態は、法律により厳格に禁止されています。これらのガイドラインに従うことは、研究と実験において法的および倫理的な基準の遵守を確実にするために重要です。