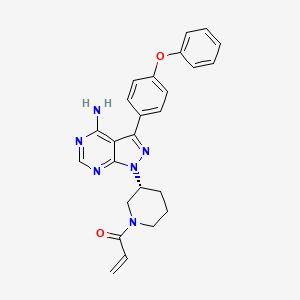
伊布替尼
描述
伊布替尼是一种小分子药物,作为布鲁顿酪氨酸激酶(BTK)的不可逆抑制剂。 它主要用于治疗各种B细胞恶性肿瘤,包括慢性淋巴细胞白血病、套细胞淋巴瘤和瓦尔登斯特伦巨球蛋白血症 . 伊布替尼于2013年11月首次获得美国食品药品监督管理局批准,此后已成为治疗B细胞癌的关键组成部分 .
作用机制
伊布替尼通过不可逆地与布鲁顿酪氨酸激酶活性位点中的半胱氨酸-481 残基结合而发挥作用。这种结合抑制BTK的激酶活性,从而阻断B细胞受体信号通路。 这种抑制导致恶性B细胞的增殖和存活减少 . 此外,伊布替尼影响其他激酶,如C-末端Src激酶,有助于其治疗效果 .
类似化合物:
阿卡拉替尼: 另一种BTK抑制剂,具有类似的作用机制,但药代动力学特性不同。
扎努替尼: 第二代BTK抑制剂,具有更高的选择性和更少的脱靶效应。
比较: 伊布替尼独特的特点是其能够不可逆地与BTK结合,从而持续抑制B细胞受体通路。 与阿卡拉替尼和扎努替尼相比,伊布替尼具有更广泛的激酶靶点,这可能导致更广泛的治疗效果,但也可能导致更高的副作用发生率 . 阿卡拉替尼和扎努替尼旨在提供更具选择性的抑制,可能在保持疗效的同时减少不良反应 .
科学研究应用
生化分析
Biochemical Properties
Ibrutinib forms a covalent bond with a cysteine residue in the active site of BTK (Cys481), leading to its inhibition . The inhibition of BTK plays a role in the B-cell receptor signaling and thus, the presence of ibrutinib prevents the phosphorylation of downstream substrates such as PLC-γ .
Cellular Effects
Ibrutinib blocks the proteins (kinases) from sending signals to the cancer cells to grow. Blocking the signals causes the cancer cells to die. This may help to stop or slow down the cancer growing . Ibrutinib also has complex immunomodulatory effects on various non-B immune cell subsets by inhibiting BTK-dependent signaling pathways of specific immune receptors .
Molecular Mechanism
Ibrutinib is a potent, irreversible inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK). The acrylamide group of ibrutinib forms a covalent bond with the cysteine residue C481 in the BTK active site, leading to sustained inhibition of BTK enzymatic activity . Ibrutinib also binds to C-terminal Src Kinases, inhibiting the kinase from promoting cell differentiation and growth .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
Ibrutinib-related adverse events are common and have resulted in discontinuation of therapy in >20% of patients taking the drug in a real-world setting . A pilot trial evaluated stepwise reduction of ibrutinib dose in patients with CLL from 420 to 280 to 140 mg/d over three 28-day cycles .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In rodent glioma models, ibrutinib (25 mg/kg) combined with doxil prolonged median survival . In another study, ibrutinib (10 mg/kg) protected against poly I:C-induced (5 mg/kg) and LPS-induced (5 mg/kg) lung inflammation .
Metabolic Pathways
The metabolism of ibrutinib is mainly performed by CYP3A5 and CYP3A4, and to a minor extent, it is seen to be performed by CYP2D6 .
Transport and Distribution
Ibrutinib is rapidly absorbed after oral administration and it presents a Cmax, tmax and AUC of approximately 35 ng/ml, 1-2 hour and 953 mg.h/ml respectively . The volume of distribution at steady-state of ibrutinib is approximately 10,000 L .
Subcellular Localization
Resistance to ibrutinib can be conferred via aberrant nuclear/cytoplasmic subcellular localization of FOXO3a . Ibrutinib induces nuclear retention of IκB that was accompanied by the reduction of DNA-binding activity of NFκB, suggesting that NFκB is trapped in an inhibitory complex .
准备方法
合成路线和反应条件: 伊布替尼的合成涉及几个关键步骤:
缩合和甲氧基化: 4-苄氧基苯甲酰氯与丙二腈和硫酸二甲酯反应生成4-苄氧基苯基(甲氧基)亚乙烯二氰基甲烷。
吡唑环化: 然后将中间体与1-(3R-肼基-1-哌啶基)-2-丙烯-1-酮进行吡唑环化,形成1-[(3R)-[3-(4-苄氧基苯基)-4-腈基-5-氨基-1H-吡唑]-1-哌啶基]-2-丙烯-1-酮。
嘧啶环化: 最后,发生嘧啶环化反应生成伊布替尼
工业生产方法: 伊布替尼的工业生产通常涉及使用上述步骤进行大规模合成,并针对产量和纯度进行优化。 该过程可能包括额外的纯化步骤,如重结晶和色谱,以确保最终产品符合药典标准 .
反应类型:
氧化: 伊布替尼可以发生氧化反应,特别是在苯氧基苯基部分。
还原: 还原反应可能会针对分子中存在的腈基。
取代: 亲核取代反应可能发生在哌啶环上。
常用试剂和条件:
氧化: 常见的氧化剂包括过氧化氢和高锰酸钾。
还原: 使用如氢化铝锂和硼氢化钠等还原剂。
主要产物: 从这些反应形成的主要产物取决于所使用的特定条件和试剂。 例如,氧化可能产生羟基化衍生物,而还原可以产生胺衍生物 .
相似化合物的比较
Acalabrutinib: Another BTK inhibitor with a similar mechanism of action but different pharmacokinetic properties.
Zanubrutinib: A second-generation BTK inhibitor with improved selectivity and reduced off-target effects.
Tirabrutinib: A BTK inhibitor used in the treatment of B-cell malignancies with a focus on reducing adverse effects
Comparison: Ibrutinib is unique in its ability to irreversibly bind to BTK, providing sustained inhibition of the B-cell receptor pathway. Compared to acalabrutinib and zanubrutinib, ibrutinib has a broader range of kinase targets, which can lead to a wider spectrum of therapeutic effects but also a higher potential for side effects . Acalabrutinib and zanubrutinib are designed to offer more selective inhibition, potentially reducing adverse effects while maintaining efficacy .
属性
IUPAC Name |
1-[(3R)-3-[4-amino-3-(4-phenoxyphenyl)pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-1-yl]piperidin-1-yl]prop-2-en-1-one | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C25H24N6O2/c1-2-21(32)30-14-6-7-18(15-30)31-25-22(24(26)27-16-28-25)23(29-31)17-10-12-20(13-11-17)33-19-8-4-3-5-9-19/h2-5,8-13,16,18H,1,6-7,14-15H2,(H2,26,27,28)/t18-/m1/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
XYFPWWZEPKGCCK-GOSISDBHSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C=CC(=O)N1CCCC(C1)N2C3=NC=NC(=C3C(=N2)C4=CC=C(C=C4)OC5=CC=CC=C5)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C=CC(=O)N1CCC[C@H](C1)N2C3=NC=NC(=C3C(=N2)C4=CC=C(C=C4)OC5=CC=CC=C5)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C25H24N6O2 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID60893450 | |
| Record name | Ibrutinib | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60893450 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
440.5 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Solubility |
Practically insoluble in water, Freely soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide; soluble in methanol | |
| Record name | Ibrutinib | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09053 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | IBRUTINIB | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/8260 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Ibrutinib is an inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK). It forms a covalent bond with a cysteine residue in the active site of BTK (Cys481), leading to its inhibition. The inhibition of BTK plays a role in the B-cell receptor signaling and thus, the presence of ibrutinib prevents the phosphorylation of downstream substrates such as PLC-γ., Ibrutinib is a novel oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor that irreversibly binds and inhibits tyrosine-protein kinase BTK (Bruton tyrosine kinase). BTK has been found to be important in the function of B-cell receptor signaling and therefore in the maintenance and expansion of various B-cell malignancies including chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). Targeting BTK with ibrutinib has been found to be an effective strategy in treating these malignancies. Phase I clinical testing in non-Hodgkin's lymphomas and CLL showed that the drug was extremely well tolerated with no major dose-limiting toxicities and a 54% overall response rate. Subsequently, two phase Ib/II studies were performed on patients with CLL, one in relapsed/refractory CLL and one in previously untreated elderly patients with CLL. Both of these studies continued to show good tolerability of the drug and an overall response rate of about 71% with extended duration of response. Another phase II study using ibrutinib in relapsed/refractory MCL was conducted and also showed that it was well tolerated with an overall response rate of 68% and extended duration of response. Due to these results, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration granted accelerated approval for ibrutinib in November 2013 for patients with MCL who had received at least one prior therapy and in February 2014 for patients with CLL who had received at least one prior therapy. This review will discuss the preclinical pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and clinical efficacy to date of ibrutinib in the treatment of CLL and MCL., ... In this study we report for the first time that ibrutinib is cytotoxic to malignant plasma cells from patients with multiple myeloma (MM) and furthermore that treatment with ibrutinib significantly augments the cytotoxic activity of bortezomib and lenalidomide chemotherapies. We describe that the cytotoxicity of ibrutinib in MM is mediated via an inhibitory effect on the nuclear factor-(k)B (NF-(k)B) pathway. Specifically, ibrutinib blocks the phosphorylation of serine-536 of the p65 subunit of NF-(k)B, preventing its nuclear translocation, resulting in down-regulation of anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-xL, FLIP(L) and survivin and culminating in caspase-mediated apoptosis within the malignant plasma cells...., Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is an aggressive B-cell malignancy that characteristically shows overexpression of cyclin-D1 due to an alteration in the t(11;14)(q13;q32) chromosomal region. Although there are some promising treatment modalities, great majority of patients with this disease remain incurable. The B-cell antigen receptor (BCR) signaling plays a crucial role in B-cell biology and lymphomagenesis. Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) has been identified as a key component of the BCR signaling pathway. Evidence suggests that the blockade of BTK activity by potent pharmacologic inhibitors attenuates BCR signaling and induces cell death. Notably, the expression levels and the role of BTK in MCL survival are still elusive. Here, we demonstrated a moderate to strong BTK expression in all MCL cases (n=19) compared to benign lymphoid tissues. Treatment of MCL cell lines (Mino or Jeko-1) with a potent BTK pharmacologic inhibitor, Ibrutinib, decreased phospho-BTK-Tyr(223) expression. Consistent with this observation, Ibrutinib inhibited the viability of both Mino and JeKo-1 cells in concentration- and time-dependent manners. Ibrutinib also induced a concentration-dependent apoptosis in both cell lines. Consistently, Ibrutinib treatment decreased the levels of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and Mcl-1 protein. These findings suggest that BTK signaling plays a critical role in MCL cell survival, and the targeting of BTK could represent a promising therapeutic modality for aggressive lymphoma., Ibrutinib is a small-molecule inhibitor of Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK). Ibrutinib forms a covalent bond with a cysteine residue in the BTK active site, leading to inhibition of BTK enzymatic activity. BTK is a signaling molecule of the B-cell antigen receptor (BCR) and cytokine receptor pathways. BTK's role in signaling through the B-cell surface receptors results in activation of pathways necessary for B-cell trafficking, chemotaxis, and adhesion. Nonclinical studies show that ibrutinib inhibits malignant B-cell proliferation and survival in vivo as well as cell migration and substrate adhesion in vitro. | |
| Record name | Ibrutinib | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09053 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | IBRUTINIB | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/8260 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
White to off-white solid | |
CAS No. |
936563-96-1 | |
| Record name | Ibrutinib | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=936563-96-1 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Ibrutinib [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0936563961 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Ibrutinib | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09053 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Ibrutinib | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60893450 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | 1-[(3R)-3-[4-amino-3-(4-phenoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-1-yl]piperidin-1-yl]prop-2-en-1-one | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | IBRUTINIB | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/1X70OSD4VX | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | IBRUTINIB | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/8260 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Melting Point |
149-158ºC | |
| Record name | Ibrutinib | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09053 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
体外研究产品的免责声明和信息
请注意,BenchChem 上展示的所有文章和产品信息仅供信息参考。 BenchChem 上可购买的产品专为体外研究设计,这些研究在生物体外进行。体外研究,源自拉丁语 "in glass",涉及在受控实验室环境中使用细胞或组织进行的实验。重要的是要注意,这些产品没有被归类为药物或药品,他们没有得到 FDA 的批准,用于预防、治疗或治愈任何医疗状况、疾病或疾病。我们必须强调,将这些产品以任何形式引入人类或动物的身体都是法律严格禁止的。遵守这些指南对确保研究和实验的法律和道德标准的符合性至关重要。


![12,14-dimethyl-9-(5-methylfuran-2-yl)-17-phenyl-1,8,12,14-tetrazatetracyclo[8.7.0.02,7.011,16]heptadeca-2,4,6,10,16-pentaene-13,15-dione](/img/structure/B1684367.png)
![N-[(1R,2R)-1-(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-6-yl)-1-hydroxy-3-pyrrolidin-1-ylpropan-2-yl]nonanamide](/img/structure/B1684369.png)
![2-methyl-N-[2-methyl-4-[(2-methylphenyl)diazenyl]phenyl]pyrazole-3-carboxamide](/img/structure/B1684373.png)