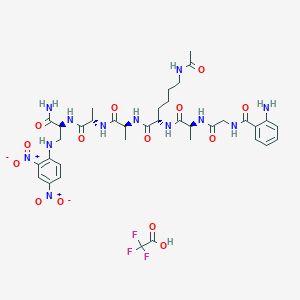
H-His-Gly-Glu-Gly-aThr-Phe-aThr-Ser-Asp-Val-Ser-Ser-Tyr-Leu-Glu-Gly-Gln-D-Ala-D-Ala-Lys-Glu-Phe-aIle-D-Ala-Trp-Leu-Val-Lys-Gly-Arg-NH2
描述
艾尔比格鲁肽是一种用于治疗2型糖尿病的胰高血糖素样肽-1受体激动剂。它在欧洲以Eperzan的商品名销售,在美国以Tanzeum的商品名销售。 艾尔比格鲁肽是重组DNA产生的、类似于人胰高血糖素样肽-1的多肽类似物,旨在增强葡萄糖依赖性胰岛素分泌,抑制不适当的胰高血糖素分泌,延缓胃排空,并减少食物摄入 .
作用机制
艾尔比格鲁肽作为胰高血糖素样肽-1受体的激动剂起作用。该受体激活导致胰腺β细胞葡萄糖依赖性胰岛素分泌增加。此外,艾尔比格鲁肽抑制胰高血糖素分泌,延缓胃排空,并促进饱腹感。 这些综合效应有助于调节血糖水平 .
生化分析
Biochemical Properties
Albiglutide acts as an agonist at the GLP-1 receptor, which makes it a type of incretin mimetic . This causes an increase in insulin secretion, predominantly in the presence of high blood glucose, and also slows down gastric emptying .
Cellular Effects
Albiglutide has a significant impact on various types of cells and cellular processes. It influences cell function by increasing insulin secretion, predominantly in the presence of high blood glucose . This can have a profound effect on cell signaling pathways, gene expression, and cellular metabolism.
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of action of Albiglutide involves its role as an agonist of the GLP-1 receptor . This interaction leads to an increase in insulin secretion, predominantly in the presence of high blood glucose. It also slows down gastric emptying, which can have a significant impact on the body’s metabolic processes .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
It is known that Albiglutide has a half-life of 5 (4–7) days , indicating its stability and potential for long-term effects on cellular function.
Metabolic Pathways
Albiglutide is involved in the incretin metabolic pathway, where it acts as an agonist of the GLP-1 receptor . This interaction leads to an increase in insulin secretion, predominantly in the presence of high blood glucose, and also slows down gastric emptying .
准备方法
合成路线和反应条件: 艾尔比格鲁肽是使用重组DNA技术合成的。该过程涉及将编码艾尔比格鲁肽多肽的基因插入合适的表达载体中,然后将其导入宿主细胞,通常是大肠杆菌或酵母菌。 宿主细胞在特定条件下培养以表达艾尔比格鲁肽多肽,然后通过一系列色谱技术进行纯化 .
工业生产方法: 艾尔比格鲁肽的工业生产遵循类似的重组DNA方法,但规模更大。生产过程包括发酵、细胞裂解、蛋白质提取和纯化。 最终产品被配制成皮下注射剂供临床使用 .
化学反应分析
反应类型: 艾尔比格鲁肽主要在体内发生蛋白水解降解。 由于其肽性质,它不会参与典型的化学反应,如氧化、还原或取代 .
常用试剂和条件: 艾尔比格鲁肽的降解涉及蛋白酶的酶促裂解。 这些反应的特定条件是生理性的,发生在人体内 .
形成的主要产物: 艾尔比格鲁肽降解形成的主要产物是更小的肽片段和氨基酸,这些产物会被进一步代谢或排泄 .
科学研究应用
相似化合物的比较
艾尔比格鲁肽属于一类称为胰高血糖素样肽-1受体激动剂的药物。该类药物中的类似化合物包括利拉鲁肽、艾塞那肽、度拉鲁肽和司美格鲁肽。
比较:
利拉鲁肽: 与艾尔比格鲁肽相比,利拉鲁肽的半衰期更短,需要每天服用,而艾尔比格鲁肽每周服用一次.
艾塞那肽: 艾塞那肽是另一种胰高血糖素样肽-1受体激动剂,作用时间更短,需要根据制剂的不同每天服用两次或每周服用一次.
独特性: 艾尔比格鲁肽的独特之处在于它与人血清白蛋白融合,从而延长了其半衰期,并允许每周服用一次。 这种融合还降低了与其他胰高血糖素样肽-1受体激动剂相比的免疫原性风险 .
属性
IUPAC Name |
(4S)-5-[[2-[[(2S,3S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S,3S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[2-[[(2S)-5-amino-1-[[(2R)-1-[[(2R)-1-[[(2S)-6-amino-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S,3R)-1-[[(2R)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-6-amino-1-[[2-[[(2S)-1-amino-5-carbamimidamido-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]amino]-1-oxohexan-2-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-4-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl]amino]-4-carboxy-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxohexan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-1,5-dioxopentan-2-yl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]amino]-4-carboxy-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-4-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-3-hydroxy-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-3-hydroxy-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-3-carboxy-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-3-hydroxy-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-3-hydroxy-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl]amino]-3-hydroxy-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]amino]-4-[[2-[[(2S)-2-amino-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)propanoyl]amino]acetyl]amino]-5-oxopentanoic acid | |
|---|---|---|
| Details | Computed by Lexichem TK 2.7.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C148H224N40O45/c1-16-76(10)119(145(231)166-79(13)125(211)174-103(59-85-62-158-90-35-24-23-34-88(85)90)135(221)176-99(55-73(4)5)136(222)185-117(74(6)7)143(229)173-92(36-25-27-51-149)127(213)160-65-109(196)167-91(122(153)208)38-29-53-157-148(154)155)187-137(223)101(56-82-30-19-17-20-31-82)177-132(218)97(46-50-115(204)205)172-131(217)93(37-26-28-52-150)170-124(210)78(12)164-123(209)77(11)165-130(216)96(43-47-108(152)195)169-111(198)66-161-129(215)95(45-49-114(202)203)171-133(219)98(54-72(2)3)175-134(220)100(58-84-39-41-87(194)42-40-84)178-140(226)105(68-189)181-142(228)107(70-191)182-144(230)118(75(8)9)186-139(225)104(61-116(206)207)179-141(227)106(69-190)183-147(233)121(81(15)193)188-138(224)102(57-83-32-21-18-22-33-83)180-146(232)120(80(14)192)184-112(199)67-162-128(214)94(44-48-113(200)201)168-110(197)64-159-126(212)89(151)60-86-63-156-71-163-86/h17-24,30-35,39-42,62-63,71-81,89,91-107,117-121,158,189-194H,16,25-29,36-38,43-61,64-70,149-151H2,1-15H3,(H2,152,195)(H2,153,208)(H,156,163)(H,159,212)(H,160,213)(H,161,215)(H,162,214)(H,164,209)(H,165,216)(H,166,231)(H,167,196)(H,168,197)(H,169,198)(H,170,210)(H,171,219)(H,172,217)(H,173,229)(H,174,211)(H,175,220)(H,176,221)(H,177,218)(H,178,226)(H,179,227)(H,180,232)(H,181,228)(H,182,230)(H,183,233)(H,184,199)(H,185,222)(H,186,225)(H,187,223)(H,188,224)(H,200,201)(H,202,203)(H,204,205)(H,206,207)(H4,154,155,157)/t76-,77-,78-,79-,80+,81+,89+,91+,92+,93+,94+,95+,96+,97+,98+,99+,100+,101+,102+,103+,104+,105+,106+,107+,117+,118+,119+,120+,121+/m1/s1 | |
| Details | Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
JYDZPPZAYQTOIV-OTSUTHPESA-N | |
| Details | Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CCC(C)C(C(=O)NC(C)C(=O)NC(CC1=CNC2=CC=CC=C21)C(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C(=O)NC(C(C)C)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NCC(=O)NC(CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)N)NC(=O)C(CC3=CC=CC=C3)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CCCCN)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)N)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC4=CC=C(C=C4)O)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(C(C)O)NC(=O)C(CC5=CC=CC=C5)NC(=O)C(C(C)O)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(CC6=CN=CN6)N | |
| Details | Computed by OEChem 2.3.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CC[C@@H](C)[C@@H](C(=O)N[C@H](C)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC1=CNC2=CC=CC=C21)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC(C)C)C(=O)N[C@@H](C(C)C)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCCCN)C(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@@H](CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)N)NC(=O)[C@H](CC3=CC=CC=C3)NC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CCCCN)NC(=O)[C@@H](C)NC(=O)[C@@H](C)NC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)N)NC(=O)CNC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CC(C)C)NC(=O)[C@H](CC4=CC=C(C=C4)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CO)NC(=O)[C@H](CO)NC(=O)[C@H](C(C)C)NC(=O)[C@H](CC(=O)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CO)NC(=O)[C@H]([C@H](C)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CC5=CC=CC=C5)NC(=O)[C@H]([C@H](C)O)NC(=O)CNC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)CNC(=O)[C@H](CC6=CN=CN6)N | |
| Details | Computed by OEChem 2.3.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C148H224N40O45 | |
| Details | Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Weight |
3283.6 g/mol | |
| Details | Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Albiglutide is an agonist of the GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide 1) receptor and augments glucose-dependent insulin secretion. Albiglutide also slows gastric emptying., Tanzeum is an agonist of the GLP-1 receptor and augments glucose-dependent insulin secretion. Tanzeum also slows gastric emptying. | |
| Details | NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Tanzeum (Albiglutide) Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution (Updated: May 2015). Available from, as of November 20, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=5fcad939-76e7-49cf-af94-4e6aef17901f | |
| Record name | Albiglutide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09043 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Details | NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Tanzeum (Albiglutide) Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution (Updated: May 2015). Available from, as of November 20, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=5fcad939-76e7-49cf-af94-4e6aef17901f | |
| Record name | Albiglutide | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/8282 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
White to yellow powder | |
CAS No. |
782500-75-8 | |
| Record name | Albiglutide [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0782500758 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Albiglutide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09043 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Albiglutide | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/8282 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Q1: What is the mechanism of action of albiglutide?
A1: Albiglutide is a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA). [] It exerts its therapeutic effect by binding to and activating GLP-1 receptors. [, , ] This activation triggers a cascade of downstream effects, primarily in the pancreas:
- Increased Insulin Secretion: Albiglutide enhances glucose-dependent insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells. [, , ] This means insulin release is amplified when blood glucose levels are elevated, such as after a meal.
- Decreased Glucagon Secretion: Simultaneously, albiglutide suppresses glucagon secretion from pancreatic α-cells. [, , ] Glucagon normally raises blood glucose levels; therefore, its suppression contributes to improved glycemic control.
Q2: What are the additional effects of albiglutide beyond the pancreas?
A2: In addition to its pancreatic effects, albiglutide influences other physiological processes:
- Delayed Gastric Emptying: Albiglutide slows down the rate at which food empties from the stomach into the small intestine. [, , ] This contributes to a feeling of fullness and can help regulate post-meal blood glucose levels.
- Increased Satiety: Albiglutide acts on the central nervous system to promote a sense of satiety or fullness, further contributing to its potential for weight management. [, , ]
Q3: What is the molecular structure of albiglutide?
A4: Albiglutide is a large molecule comprised of two identical chains of modified human glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) linked to a recombinant human albumin molecule. [, , ] The specific modifications within the GLP-1 chains confer resistance to DPP-4 degradation, a key factor in its extended half-life.
Q4: What are the molecular formula and weight of albiglutide?
A4: Due to the complexity of albiglutide's structure as a fusion protein, providing a precise molecular formula and weight is not straightforward. It's more relevant to consider its amino acid sequence and modifications when understanding its properties.
Q5: Is there spectroscopic data available for albiglutide?
A5: Spectroscopic data, such as that from nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) or mass spectrometry, is crucial for characterizing protein structure. While publicly available research articles may not always provide this detailed data, it's likely utilized during the drug development process to confirm albiglutide's identity, purity, and structural integrity.
Q6: How is albiglutide absorbed and distributed in the body?
A7: Following subcutaneous administration, albiglutide is primarily absorbed via the lymphatic circulation. [] Its distribution is largely influenced by its fusion to human albumin, a protein abundant in plasma. This fusion contributes to its long half-life and allows for once-weekly dosing. [, , ]
Q7: How is albiglutide metabolized and excreted?
A8: As a large peptide, albiglutide's metabolism differs from small molecule drugs. It's likely broken down into smaller peptides and amino acids through proteolysis, a process involving enzymes. While specific details on its metabolic pathways may not be extensively published, its elimination half-life of approximately 5 days suggests a slow clearance process. [, ]
Q8: How does albiglutide affect glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes?
A9: Clinical trials consistently demonstrate albiglutide's efficacy in lowering both fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and postprandial plasma glucose (PPG), with HbA1c reductions ranging from -0.55% to -0.9%. [, , , , , , , , ] This glucose-lowering effect is attributed to its multi-faceted mechanism involving increased insulin secretion, decreased glucagon secretion, and delayed gastric emptying. [, , , ]
Q9: Does albiglutide cause weight loss?
A10: While albiglutide doesn't typically cause significant weight loss compared to placebo, clinical trials have shown it can lead to modest weight reductions ranging from +0.28 to -1.21 kg, depending on the comparator drug and study population. [, , , , , , , , ] Its weight management potential is attributed to its ability to increase satiety and slow gastric emptying. [, , ]
Q10: Has albiglutide been tested in preclinical models?
A11: Yes, preclinical studies in rats have demonstrated albiglutide's protective effects against ischemia/reperfusion injury, a condition that deprives the heart of oxygen. [] The study found that albiglutide significantly reduced infarct size and improved cardiac function and energetics post-injury. [] These benefits were associated with enhanced myocardial glucose uptake and a shift towards a more favorable cardiac metabolism. []
Q11: What were the main findings of the HARMONY clinical trial program?
A12: The HARMONY program encompassed eight Phase III clinical trials, representing a comprehensive evaluation of albiglutide's efficacy and safety in various patient populations with type 2 diabetes. [, , , , , , , ] These trials compared albiglutide to placebo, other GLP-1 receptor agonists, and other classes of diabetes medications, revealing key findings:
- Superior Glycemic Control: Albiglutide consistently demonstrated superior reductions in HbA1c and fasting plasma glucose compared to placebo and certain active comparators, including sitagliptin and glimepiride. [, , , , , , , ]
- Weight Management: While not as potent as some other GLP-1RAs in this regard, albiglutide demonstrated either weight neutrality or modest weight loss in some trials. [, , , , , , , ]
- Cardiovascular Safety: A key concern with diabetes medications is their potential impact on cardiovascular health. The HARMONY Outcomes trial, a major component of the program, investigated albiglutide's cardiovascular safety in patients with established cardiovascular disease. [] Notably, it demonstrated a 25% relative risk reduction in myocardial infarction (heart attack) across various infarction types. []
Q12: What is the safety profile of albiglutide?
A13: In clinical trials, albiglutide demonstrated a generally favorable safety and tolerability profile. [, , , , , , , , ] The most common adverse events were gastrointestinal in nature, primarily:
- Nausea: Experienced by a greater proportion of patients receiving albiglutide compared to placebo, but generally mild to moderate in severity. [, , ]
- Diarrhea: Similar in incidence to nausea, typically mild to moderate, and often resolving with continued treatment. [, , ]
- Injection Site Reactions: Reported in a smaller percentage of patients, typically characterized by redness or mild pain at the injection site. [, , ]
Q13: Are there any serious safety concerns associated with albiglutide?
A14: While albiglutide is generally well-tolerated, there have been rare reports of pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) associated with its use. [, , ] Patients with a history of pancreatitis should avoid albiglutide. [, , ] Additionally, as with other GLP-1RAs, a potential risk for thyroid C-cell tumors has been observed in rodent studies, though it remains unclear whether this translates to humans. [] Albiglutide is contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2. []
体外研究产品的免责声明和信息
请注意,BenchChem 上展示的所有文章和产品信息仅供信息参考。 BenchChem 上可购买的产品专为体外研究设计,这些研究在生物体外进行。体外研究,源自拉丁语 "in glass",涉及在受控实验室环境中使用细胞或组织进行的实验。重要的是要注意,这些产品没有被归类为药物或药品,他们没有得到 FDA 的批准,用于预防、治疗或治愈任何医疗状况、疾病或疾病。我们必须强调,将这些产品以任何形式引入人类或动物的身体都是法律严格禁止的。遵守这些指南对确保研究和实验的法律和道德标准的符合性至关重要。


![Gal|A(1-3)[Neu5Ac|A(2-6)]GlcNAc-|A-pNP](/img/structure/B3029696.png)