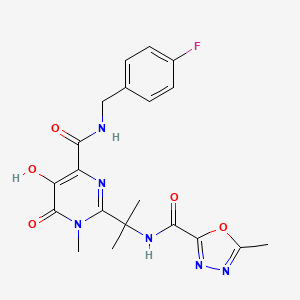
拉替拉韦
描述
拉替拉韦是一种抗逆转录病毒药物,与其他药物联合使用以治疗人类免疫缺陷病毒 (HIV) 感染。 它是第一个获批的 HIV 整合酶链转移抑制剂,它阻断 HIV 整合酶的功能,整合酶是病毒复制所必需的一种酶 。 拉替拉韦于 2007 年在美国获准用于医疗用途,并列入世界卫生组织基本药物清单 .
作用机制
拉替拉韦抑制 HIV 整合酶的催化活性,阻止病毒基因组整合到人类基因组中。这种抑制阻止了 HIV-1 整合的链转移步骤,该步骤对于病毒复制至关重要。 拉替拉韦主要通过葡萄糖醛酸化代谢 .
科学研究应用
生化分析
Biochemical Properties
Raltegravir plays a significant role in biochemical reactions as it inhibits HIV integrase, a key enzyme in the HIV life cycle . This enzyme is responsible for the integration of the HIV-1 viral DNA, generated by reverse transcription of the RNA genome, into the host cell chromosomes . By inhibiting this process, Raltegravir prevents the replication of the virus .
Cellular Effects
Raltegravir has a profound impact on various types of cells infected with HIV-1. By inhibiting the integrase enzyme, it prevents the integration of the viral DNA into the host cell chromosomes . This halts the production of new viruses, thereby influencing cell function and impacting cellular processes such as cell signaling pathways, gene expression, and cellular metabolism .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of Raltegravir involves the inhibition of the HIV integrase enzyme to prevent the viral genome from being incorporated into the human genome . Raltegravir is primarily metabolized by glucuronidation .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, Raltegravir has shown potent antiretroviral activity and is well tolerated in HIV-1–infected individuals . Specific resistance mutations have been identified in patients failing to respond to treatment with Raltegravir
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In animal models, the effects of Raltegravir have been observed to vary with different dosages . More detailed studies are required to understand the threshold effects and any toxic or adverse effects at high doses.
Metabolic Pathways
Raltegravir is involved in metabolic pathways where it is primarily metabolized by glucuronidation . This metabolic process does not involve the liver, thus reducing the potential for drug-drug interactions .
Transport and Distribution
It is known that Raltegravir is approximately 83% bound to human plasma protein and is minimally distributed into red blood cells .
Subcellular Localization
Given its mechanism of action, it can be inferred that Raltegravir acts in the nucleus of the cell where it prevents the integration of the HIV-1 viral DNA into the host cell chromosomes .
准备方法
拉替拉韦通过一个多步骤过程合成,涉及多个关键中间体。其合成中的一个重大挑战是嘧啶酮中间体的选择性 N-甲基化。 合成路线通常包括以下步骤 :
N-烷基化: 使用 (氯甲基) 二甲基氯硅烷和氟化钾对嘧啶酮中间体进行烷基化。
酰胺化: 烷基化中间体与胺进行酰胺化。
脱硅烷化: 最后一步涉及使用甲醇中的氟化钾进行脱硅烷化。
工业生产方法涉及优化这些步骤以实现高收率和纯度。 该过程被放大以生产拉替拉韦钾,它是药物中使用的药学活性形式 .
化学反应分析
拉替拉韦会发生各种化学反应,包括:
氧化: 在特定条件下,拉替拉韦可以被氧化,导致形成各种氧化产物。
还原: 可以在拉替拉韦上进行还原反应以改变其官能团。
取代: 拉替拉韦可以发生取代反应,尤其是在氟苄基上。
这些反应中常用的试剂包括过氧化氢等氧化剂、硼氢化钠等还原剂以及用于取代反应的亲核试剂。 形成的主要产物取决于所用反应条件和试剂 .
相似化合物的比较
拉替拉韦与其他整合酶链转移抑制剂 (INSTIs) 相比,例如艾维拉韦、多替拉韦、比克替拉韦和卡博替拉韦。 这些化合物具有相似的作用机制,但在药代动力学和药效学特性方面有所不同 :
艾维拉韦: 需要与考比西他联合使用才能获得有效的血浆浓度。
多替拉韦: 以其耐药性高和一天一次的剂量而闻名。
比克替拉韦: 与恩曲他滨和替诺福韦艾拉酚胺以单片剂方案联合使用。
卡博替拉韦: 以长效注射剂形式提供。
属性
IUPAC Name |
N-[2-[4-[(4-fluorophenyl)methylcarbamoyl]-5-hydroxy-1-methyl-6-oxopyrimidin-2-yl]propan-2-yl]-5-methyl-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2-carboxamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C20H21FN6O5/c1-10-25-26-17(32-10)16(30)24-20(2,3)19-23-13(14(28)18(31)27(19)4)15(29)22-9-11-5-7-12(21)8-6-11/h5-8,28H,9H2,1-4H3,(H,22,29)(H,24,30) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
CZFFBEXEKNGXKS-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC1=NN=C(O1)C(=O)NC(C)(C)C2=NC(=C(C(=O)N2C)O)C(=O)NCC3=CC=C(C=C3)F | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C20H21FN6O5 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID2048660 | |
| Record name | Raltegravir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID2048660 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
444.4 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Raltegravir inhibits HIV integrase to prevent the viral genome being incorporated into the human genome. Raltegravir is primarily metabolized by glucuronidation., Raltegravir inhibits the catalytic activity of HIV-1 integrase, an HIV-1 encoded enzyme that is required for viral replication. Inhibition of integrase prevents the covalent insertion, or integration, of unintegrated linear HIV-1 DNA into the host cell genome preventing the formation of the HIV-1 provirus. The provirus is required to direct the production of progeny virus, so inhibiting integration prevents propagation of the viral infection. Raltegravir did not significantly inhibit human phosphoryltransferases including DNA polymerases alpha, beta, and gamma. | |
| Record name | Raltegravir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB06817 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Raltegravir | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/8124 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
CAS No. |
518048-05-0 | |
| Record name | Raltegravir | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=518048-05-0 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Raltegravir [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0518048050 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Raltegravir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB06817 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Raltegravir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID2048660 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | N-[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-1,6-dihydro-5-hydroxy-1-methyl-2-[1-methyl-1-[[(5-methyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)carbonyl]amino]ethyl]-6-oxo-4-pyrimidinecarboxamide | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.124.631 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | RALTEGRAVIR | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/22VKV8053U | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Raltegravir | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/8124 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Synthesis routes and methods
Procedure details





Q1: How does Raltegravir exert its antiretroviral effect?
A1: Raltegravir is a potent inhibitor of HIV-1 integrase, specifically targeting the strand transfer step of the viral integration process. [] This prevents the integration of the viral genome into the host cell's DNA, a crucial step for viral replication. [, ]
Q2: What is the consequence of inhibiting HIV-1 integrase?
A2: Blocking the strand transfer step by Raltegravir leads to the accumulation of unintegrated viral DNA in the cytoplasm of infected cells. [, ] This ultimately prevents the production of new infectious viral particles, effectively suppressing viral replication. [, , ]
Q3: What is the significance of Raltegravir's target in the HIV life cycle?
A3: HIV-1 integrase is a viral enzyme essential for viral replication and is not found in human cells. [] Targeting this unique enzyme offers a high degree of selectivity, minimizing the potential for adverse effects on host cell processes. []
Q4: What is the molecular formula and weight of Raltegravir?
A4: This information is not provided in the provided scientific papers. Please consult comprehensive chemical databases like PubChem or DrugBank for detailed structural information.
Q5: How stable is Raltegravir under various storage conditions?
A5: While the provided research doesn't specify exact storage conditions, one study mentions that high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was used to measure Raltegravir trough concentrations, suggesting it maintains stability in biological samples for analysis. [] Further research on its stability under different environmental conditions (temperature, humidity, light) would be valuable.
Q6: Does Raltegravir exhibit any catalytic activity itself?
A6: No, Raltegravir is an enzyme inhibitor. It acts by binding to HIV-1 integrase and blocking its catalytic activity, specifically the strand transfer reaction required for integrating viral DNA into the host cell genome. [, ]
Q7: Have any computational studies been conducted on Raltegravir?
A7: Yes, one study used an in vitro-in vivo extrapolation model to predict Raltegravir pharmacokinetics in virtual individuals with different gastrointestinal pH profiles. [] This model successfully predicted key pharmacokinetic variables with good accuracy compared to clinical data, demonstrating the utility of computational approaches in understanding Raltegravir disposition. []
Q8: How do structural modifications of Raltegravir affect its activity?
A8: The provided research focuses primarily on Raltegravir's clinical efficacy and resistance mutations rather than exploring detailed SAR. Investigating the impact of structural changes on Raltegravir's binding affinity, inhibitory potency, and resistance profile would be an interesting avenue for future research.
Q9: What is the primary route of Raltegravir elimination in humans?
A10: Raltegravir is primarily eliminated via metabolism, specifically through glucuronidation by the enzyme UGT1A1. [] This process leads to the formation of Raltegravir glucuronide, the major metabolite, which is then excreted in urine and feces. []
Q10: Does food intake affect Raltegravir pharmacokinetics?
A11: Yes, a study investigating the effect of different meal types on Raltegravir's pharmacokinetic profile found that high-fat meals might influence the drug's absorption and distribution without affecting overall exposure. [] This highlights the importance of understanding food-drug interactions for optimizing Raltegravir therapy.
Q11: How do Raltegravir concentrations vary across different biological compartments?
A12: Research indicates that Raltegravir concentrations can vary significantly between plasma, intracellular compartments (like peripheral blood mononuclear cells), and tissues (such as cervical tissue). [, ] These differences highlight the need to consider tissue-specific drug distribution when evaluating Raltegravir's efficacy and potential for pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP). []
Q12: What factors contribute to the high inter-individual variability observed in Raltegravir pharmacokinetics?
A12: Several factors can contribute to variability in Raltegravir's pharmacokinetic profile, including:
- Genetic polymorphisms: Variations in the UGT1A1 gene, particularly the UGT1A16 and 28 alleles, may impact Raltegravir metabolism and clearance. []
- Gastrointestinal factors: Luminal pH and the presence of divalent metals, like magnesium, can influence Raltegravir absorption. [, ]
- Co-administered medications: Drug-drug interactions with medications metabolized by UGT1A1 or those altering gastrointestinal pH can alter Raltegravir exposure. [, , , ]
- Liver transplantation: Patients who have undergone liver transplantation may experience reduced Raltegravir clearance, potentially leading to higher drug exposure. []
Q13: What is the significance of Raltegravir trough concentrations?
A14: Raltegravir's virologic efficacy is best correlated with its trough concentration (C trough). [] Maintaining C trough levels above the 95% inhibitory concentration (IC95) is crucial for achieving optimal viral suppression. [, ]
Q14: How is Raltegravir's efficacy assessed in preclinical settings?
A15: Cell-based assays using TZM-bl indicator cells are used to evaluate Raltegravir's ability to inhibit HIV infection in vitro. [] Additionally, humanized mouse models, such as the humanized BLT (bone marrow-liver-thymus) mice, are valuable tools for studying Raltegravir's antiviral activity, pharmacokinetics, and efficacy in preventing vaginal HIV transmission in vivo. []
Q15: Has Raltegravir's efficacy been demonstrated in clinical trials?
A16: Yes, numerous clinical trials have established the potent and durable antiretroviral activity of Raltegravir in both treatment-naive and treatment-experienced HIV-1-infected patients. [, , , , , , ] When combined with tenofovir/emtricitabine, Raltegravir achieves viral suppression and immune restoration comparable to efavirenz-based regimens. [, ] Moreover, Raltegravir has shown effectiveness in salvage therapy for patients with multidrug-resistant HIV-1 infection. [, , , ]
Q16: What are the primary mechanisms of resistance to Raltegravir?
A17: Resistance to Raltegravir typically arises from mutations in the HIV-1 integrase gene. [, , , ] The most common mutations associated with Raltegravir resistance cluster around three main pathways:
Q17: Does cross-resistance exist between Raltegravir and other integrase inhibitors?
A18: Yes, cross-resistance can occur between Raltegravir and other integrase strand transfer inhibitors (INSTIs), such as elvitegravir and dolutegravir. [, , ] The extent of cross-resistance depends on the specific mutations present in the HIV-1 integrase gene. [, , ] For instance, mutations in the Q148 pathway often confer a higher level of resistance to Raltegravir and elvitegravir compared to dolutegravir. [, ]
Q18: Can Raltegravir resistance impact subsequent treatment options?
A19: Yes, the emergence of Raltegravir resistance mutations can limit future treatment options, particularly with other INSTIs. [, ] Therefore, it's crucial to monitor for resistance development and consider alternative antiretroviral agents when appropriate.
Q19: Does Raltegravir retain any antiviral activity against resistant HIV-1 strains?
A20: Studies suggest that Raltegravir might have limited to no residual antiviral activity against HIV-1 strains harboring major resistance mutations. [, ] This finding raises questions about the benefit of maintaining Raltegravir in salvage regimens for patients with documented resistance. []
体外研究产品的免责声明和信息
请注意,BenchChem 上展示的所有文章和产品信息仅供信息参考。 BenchChem 上可购买的产品专为体外研究设计,这些研究在生物体外进行。体外研究,源自拉丁语 "in glass",涉及在受控实验室环境中使用细胞或组织进行的实验。重要的是要注意,这些产品没有被归类为药物或药品,他们没有得到 FDA 的批准,用于预防、治疗或治愈任何医疗状况、疾病或疾病。我们必须强调,将这些产品以任何形式引入人类或动物的身体都是法律严格禁止的。遵守这些指南对确保研究和实验的法律和道德标准的符合性至关重要。
![3-Pyridinesulfonamide, 6-[3-cyano-6-ethyl-5-fluoro-1-(2-pyrimidinyl)-1H-indol-2-yl]-N-[(1S)-2,2,2-trifluoro-1-methylethyl]-](/img/structure/B610331.png)
![Methyl 3-[[4-(tert-butylamino)-2-methoxyphenyl]sulfamoyl]thiophene-2-carboxylate](/img/structure/B610334.png)

![1-[(Z)-4-amino-2-fluorobut-2-enyl]-3-[3-(dimethylsulfamoyl)phenyl]-2-methylindole-5-carboxylic acid;hydrochloride](/img/structure/B610345.png)