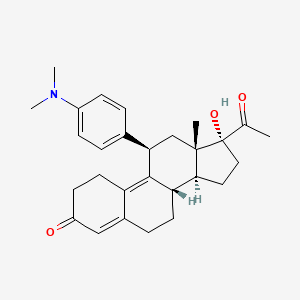
Ulipristal
Vue d'ensemble
Description
L’ulipristal est un modulateur sélectif des récepteurs de la progestérone utilisé principalement pour la contraception d’urgence et le traitement des fibromes utérins. Il s’agit d’un dérivé de la 19-norprogestérone et présente à la fois une activité antagoniste et une activité agoniste partielle au niveau du récepteur de la progestérone .
Mécanisme D'action
L’ulipristal exerce ses effets en se liant au récepteur de la progestérone, où il agit à la fois comme un antagoniste et un agoniste partiel. Cette liaison inhibe l’ovulation en empêchant la rupture folliculaire et peut également affecter l’endomètre pour empêcher l’implantation de l’embryon . Les cibles moléculaires comprennent le récepteur de la progestérone et, dans une moindre mesure, le récepteur des glucocorticoïdes .
Analyse Biochimique
Biochemical Properties
Ulipristal plays a significant role in biochemical reactions by interacting with various enzymes, proteins, and other biomolecules. It binds to the progesterone receptor, exhibiting both antagonistic and partial agonist activities. Additionally, this compound binds to the glucocorticoid receptor, although it has lower glucocorticoid activity compared to mifepristone . These interactions are crucial for its function as an emergency contraceptive and in the treatment of uterine fibroids.
Cellular Effects
This compound affects various types of cells and cellular processes. In the treatment of uterine fibroids, this compound reduces the size of fibroids by inhibiting cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis . It also influences cell signaling pathways, gene expression, and cellular metabolism. For instance, this compound has been shown to delay or inhibit ovulation by affecting the endometrium, which may prevent embryo implantation .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of this compound involves its binding to the progesterone receptor, where it acts as both an antagonist and partial agonist . This binding prevents progestin from binding to the receptor, thereby inhibiting or delaying ovulation . This compound also alters the normal endometrium, impairing implantation . Additionally, it inhibits the translocation of the glucocorticoid receptor to the nucleus, affecting gene expression .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, the effects of this compound change over time. This compound is rapidly absorbed, with a peak plasma concentration occurring approximately one hour after ingestion . Its stability and degradation over time have been studied, showing that it can inhibit follicular rupture and induce early endometrial bleeding in a dose-dependent manner . Long-term effects on cellular function have also been observed, including changes in endometrial maturation and progesterone-dependent markers of implantation .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of this compound vary with different dosages in animal models. A single post-ovulatory dose of this compound has been shown to impair post-fertilization events in mice, reducing the number of conceptuses and early implantation sites . High doses of this compound can cause histological and functional alterations in the uterine horns, affecting embryo-uterine interaction .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound is metabolized primarily by the enzyme CYP3A4 and to a lesser extent by CYP1A2 . It is converted into mono-demethylated (active) and di-methylated (inactive) metabolites . These metabolic pathways are crucial for its pharmacokinetics and overall efficacy.
Transport and Distribution
This compound is transported and distributed within cells and tissues, targeting the uterus, cervix, ovaries, and hypothalamus . It binds to plasma proteins with a high affinity, which influences its distribution and localization within the body . The transporters and binding proteins involved in its distribution play a significant role in its therapeutic effects.
Subcellular Localization
The subcellular localization of this compound involves its interaction with the glucocorticoid receptor, where it inhibits the receptor’s translocation to the nucleus . This inhibition affects the receptor’s activity and function, leading to changes in gene expression and cellular responses. This compound’s targeting signals and post-translational modifications direct it to specific compartments or organelles, influencing its overall activity.
Méthodes De Préparation
Voies de synthèse et conditions de réaction
La synthèse de l’ulipristal implique plusieurs étapes, à partir de la 19-norprogestéroneLes conditions de réaction impliquent généralement l’utilisation de réactifs tels que le méthyl lithium ou le réactif de Grignard méthylique pour les réactions d’addition, suivies d’étapes d’hydrolyse et de cristallisation pour purifier le produit final .
Méthodes de production industrielle
La production industrielle de l’this compound implique l’optimisation de la voie de synthèse afin d’assurer un rendement et une pureté élevés. Cela comprend le contrôle des conditions d’hydrolyse, telles que l’acidité, la température et le temps de réaction, afin d’obtenir le produit souhaité. Le produit final est purifié à l’aide de solvants tels que l’éthanol et l’isopropanol .
Analyse Des Réactions Chimiques
Types de réactions
L’ulipristal subit diverses réactions chimiques, notamment :
Oxydation : L’this compound peut être oxydé pour former différents métabolites.
Réduction : Les réactions de réduction peuvent modifier les groupes cétoniques présents dans la molécule.
Substitution : Des réactions de substitution peuvent se produire au niveau du groupe diméthylamino ou du groupe acétoxy.
Réactifs et conditions courants
Les réactifs courants utilisés dans ces réactions comprennent des agents oxydants tels que le permanganate de potassium et des agents réducteurs tels que le borohydrure de sodium. Les réactions sont généralement réalisées dans des conditions contrôlées de température et de pH afin de garantir la formation du produit souhaité .
Principaux produits formés
Les principaux produits formés à partir de ces réactions comprennent divers métabolites qui conservent la structure de base de l’this compound mais avec des modifications au niveau de groupes fonctionnels spécifiques .
Applications de la recherche scientifique
L’this compound a un large éventail d’applications de recherche scientifique :
Chimie : Utilisé comme composé modèle pour étudier les modulateurs sélectifs des récepteurs de la progestérone.
Biologie : Investigué pour ses effets sur les voies cellulaires et la liaison des récepteurs.
Médecine : Principalement utilisé pour la contraception d’urgence et le traitement des fibromes utérins.
Industrie : Utilisé dans l’industrie pharmaceutique pour le développement de pilules contraceptives et de traitements contre les fibromes .
Applications De Recherche Scientifique
Ulipristal has a wide range of scientific research applications:
Chemistry: Used as a model compound to study selective progesterone receptor modulators.
Biology: Investigated for its effects on cellular pathways and receptor binding.
Medicine: Primarily used for emergency contraception and the treatment of uterine fibroids.
Industry: Utilized in the pharmaceutical industry for the development of contraceptive pills and fibroid treatments .
Comparaison Avec Des Composés Similaires
Composés similaires
Mifépristone : Un autre antagoniste du récepteur de la progestérone utilisé pour l’avortement médicamenteux et la contraception d’urgence.
Lévonorgestrel : Un progestatif synthétique utilisé dans la contraception d’urgence et les contraceptifs hormonaux.
Unicité de l’ulipristal
L’this compound est unique par sa double activité d’antagoniste et d’agoniste partiel au niveau du récepteur de la progestérone, ce qui lui confère un profil d’efficacité et d’effets secondaires distincts par rapport à d’autres composés tels que la mifépristone et le lévonorgestrel .
Propriétés
IUPAC Name |
(8S,11R,13S,14S,17R)-17-acetyl-11-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]-17-hydroxy-13-methyl-1,2,6,7,8,11,12,14,15,16-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C28H35NO3/c1-17(30)28(32)14-13-25-23-11-7-19-15-21(31)10-12-22(19)26(23)24(16-27(25,28)2)18-5-8-20(9-6-18)29(3)4/h5-6,8-9,15,23-25,32H,7,10-14,16H2,1-4H3/t23-,24+,25-,27-,28-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
HKDLNTKNLJPAIY-WKWWZUSTSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC(=O)C1(CCC2C1(CC(C3=C4CCC(=O)C=C4CCC23)C5=CC=C(C=C5)N(C)C)C)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CC(=O)[C@]1(CC[C@@H]2[C@@]1(C[C@@H](C3=C4CCC(=O)C=C4CC[C@@H]23)C5=CC=C(C=C5)N(C)C)C)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C28H35NO3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID501025842 | |
| Record name | Ulipristal | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID501025842 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
433.6 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
The exact mechanism of action of ulipristal has been heavily debated. On one hand, the majority of official prescribing information labels, monographs, and prior research studies for ulipristal indicated as an emergency contraceptive suggest that its primary mechanism of action revolves around inhibiting or delaying ovulation by suppressing surges in LH that result in the postponement of follicular rupture. Conversely, some of the latest investigations pertaining to ulipristal's mechanism of action as an emergency contraceptive propose that it principally elicits its action by preventing embryo implantation, as opposed to preventing ovulation. Although previous investigations have shown that ulipristal essentially has the ability to prevent ovulation equivalent to placebo (ie. null effect or ability) when administered during LH peaks one to two days before ovulation, the agent still demonstrates a stable and consistently high contraceptive effect of approximately >=80% when used at this time. Subsequently, current studies attempt to investigate how ulipristal could elicit emergency contraception via ovulation prevention under circumstances where ovulation had already clearly been observed. Endometrial biopsy samples studied from such circumstances in such investigations subsequently show that the administered ulipristal causes endometrial tissue to become inhospitable and unsuitable for embryo implantation where a variety of genes characteristic of receptive, pro-gestational endometrium are downregulated. Nevertheless, most if not all proposed mechanisms commonly agree that ulipristal ultimately demonstrates its pharmacological effects by binding to human progesterone receptors and prevents natural, endogenous progesterone from occupying such receptors. Regardless, however, considering current and on-going research into ulipristal's ability to prevent embryo implantation, the notion that the medication can elicit post-fertilization effects potentially raises alerts and/or ethical debates over the use of ulipristal owing to potential abortifacient activity, which is considered to be on par or equipotent to that of mifepristone. Attention should be drawn to the fact that some prescribing information, however, such as the US FDA label for ulipristal indicated for emergency contraception, has included new supplementary commentary since 2018 that directly warns about ulipristal not being indicated for termination of existing pregnancies and suggesting that ulipristal use may confer alterations to the endometrium that may affect implantation and contribute to efficacy. In the treatment of fibroids, ulipristal has been shown to exert direct actions on fibroids reducing their size through inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis. | |
| Record name | Ulipristal | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB08867 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
159811-51-5 | |
| Record name | Ulipristal [USAN:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0159811515 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Ulipristal | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB08867 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Ulipristal | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID501025842 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | (8S,11R,13S,14S,17R)-17-acetyl-11-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]-17-hydroxy-13-methyl-1,2,6,7,8,11,12,14,15,16-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | ULIPRISTAL | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/6J5J15Q2X8 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Avertissement et informations sur les produits de recherche in vitro
Veuillez noter que tous les articles et informations sur les produits présentés sur BenchChem sont destinés uniquement à des fins informatives. Les produits disponibles à l'achat sur BenchChem sont spécifiquement conçus pour des études in vitro, qui sont réalisées en dehors des organismes vivants. Les études in vitro, dérivées du terme latin "in verre", impliquent des expériences réalisées dans des environnements de laboratoire contrôlés à l'aide de cellules ou de tissus. Il est important de noter que ces produits ne sont pas classés comme médicaments et n'ont pas reçu l'approbation de la FDA pour la prévention, le traitement ou la guérison de toute condition médicale, affection ou maladie. Nous devons souligner que toute forme d'introduction corporelle de ces produits chez les humains ou les animaux est strictement interdite par la loi. Il est essentiel de respecter ces directives pour assurer la conformité aux normes légales et éthiques en matière de recherche et d'expérimentation.


![N-[(3S)-1-({6-chloro-3-[1-(4-chlorobenzyl)-4-phenyl-1H-imidazol-5-yl]-1H-indol-2-yl}carbonyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl]-N,N',N'-trimethylpropane-1,3-diamine](/img/structure/B1683313.png)
![(7S,9S)-9-acetyl-7-[(2R,4S,5S,6S)-4-[[4-[[[(2S,3S,4S,6R)-6-[[(1S,3S)-3-acetyl-3,5,12-trihydroxy-10-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-2,4-dihydro-1H-tetracen-1-yl]oxy]-3-hydroxy-2-methyloxan-4-yl]amino]methyl]phenyl]methylamino]-5-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-6,9,11-tri](/img/structure/B1683324.png)