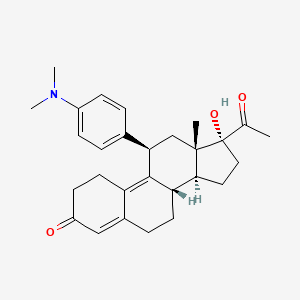
Ulipristalacetat
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Ulipristal ist ein selektiver Progesteronrezeptor-Modulator, der hauptsächlich zur Notfallkontrazeption und zur Behandlung von Uterusmyomen eingesetzt wird. Es ist ein Derivat von 19-Norprogesteron und zeigt sowohl antagonistische als auch partielle agonistische Aktivität am Progesteronrezeptor .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Ulipristal has a wide range of scientific research applications:
Chemistry: Used as a model compound to study selective progesterone receptor modulators.
Biology: Investigated for its effects on cellular pathways and receptor binding.
Medicine: Primarily used for emergency contraception and the treatment of uterine fibroids.
Industry: Utilized in the pharmaceutical industry for the development of contraceptive pills and fibroid treatments .
Wirkmechanismus
Target of Action
Ulipristal is a selective progesterone receptor modulator . It has both antagonistic and partial agonist activity at the progesterone receptor . It also binds to the glucocorticoid receptor .
Mode of Action
Ulipristal works by binding to the body’s progesterone receptors to produce an anti-progesterone effect . This interaction suppresses or delays ovulation from the ovary . It prevents progestin from binding to the progesterone receptor , thereby inhibiting or delaying ovulation . It may also alter the normal endometrium, impairing implantation .
Biochemical Pathways
The exact mechanism of action for ulipristal is still currently debated, though there is evidence that it functions by inhibiting ovulation . Some studies suggest that ulipristal may elicit activity on the endometrium that prevents embryo implantation .
Pharmacokinetics
Ulipristal acetate has good oral bioavailability and a half-life allowing one single oral administration per day for the management of fibroids . Following oral administration of a single 30 mg dose, ulipristal acetate is rapidly absorbed, with a peak plasma concentration occurring approximately 1 hour after ingestion .
Result of Action
The administration of ulipristal produces a significant decrease in the number of conceptuses compared to control . It also produces histological and functional alterations in the uterine horns, i.e., a dyssynchronous growth between endometrial glands and stroma . It impairs the ability of the uterine horns to respond to an artificial decidualization stimulus .
Action Environment
The action of ulipristal can be influenced by environmental factors such as the presence of other drugs. For example, the oral coadministration of UPA and ketoconazole reduced UPA metabolism and resulted in an approximate 2-fold increase in the average maximum plasma UPA levels and an approximate average 5.8-fold increase in bioavailability .
Biochemische Analyse
Biochemical Properties
Ulipristal plays a significant role in biochemical reactions by interacting with various enzymes, proteins, and other biomolecules. It binds to the progesterone receptor, exhibiting both antagonistic and partial agonist activities. Additionally, ulipristal binds to the glucocorticoid receptor, although it has lower glucocorticoid activity compared to mifepristone . These interactions are crucial for its function as an emergency contraceptive and in the treatment of uterine fibroids.
Cellular Effects
Ulipristal affects various types of cells and cellular processes. In the treatment of uterine fibroids, ulipristal reduces the size of fibroids by inhibiting cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis . It also influences cell signaling pathways, gene expression, and cellular metabolism. For instance, ulipristal has been shown to delay or inhibit ovulation by affecting the endometrium, which may prevent embryo implantation .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of ulipristal involves its binding to the progesterone receptor, where it acts as both an antagonist and partial agonist . This binding prevents progestin from binding to the receptor, thereby inhibiting or delaying ovulation . Ulipristal also alters the normal endometrium, impairing implantation . Additionally, it inhibits the translocation of the glucocorticoid receptor to the nucleus, affecting gene expression .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, the effects of ulipristal change over time. Ulipristal is rapidly absorbed, with a peak plasma concentration occurring approximately one hour after ingestion . Its stability and degradation over time have been studied, showing that it can inhibit follicular rupture and induce early endometrial bleeding in a dose-dependent manner . Long-term effects on cellular function have also been observed, including changes in endometrial maturation and progesterone-dependent markers of implantation .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of ulipristal vary with different dosages in animal models. A single post-ovulatory dose of ulipristal has been shown to impair post-fertilization events in mice, reducing the number of conceptuses and early implantation sites . High doses of ulipristal can cause histological and functional alterations in the uterine horns, affecting embryo-uterine interaction .
Metabolic Pathways
Ulipristal is metabolized primarily by the enzyme CYP3A4 and to a lesser extent by CYP1A2 . It is converted into mono-demethylated (active) and di-methylated (inactive) metabolites . These metabolic pathways are crucial for its pharmacokinetics and overall efficacy.
Transport and Distribution
Ulipristal is transported and distributed within cells and tissues, targeting the uterus, cervix, ovaries, and hypothalamus . It binds to plasma proteins with a high affinity, which influences its distribution and localization within the body . The transporters and binding proteins involved in its distribution play a significant role in its therapeutic effects.
Subcellular Localization
The subcellular localization of ulipristal involves its interaction with the glucocorticoid receptor, where it inhibits the receptor’s translocation to the nucleus . This inhibition affects the receptor’s activity and function, leading to changes in gene expression and cellular responses. Ulipristal’s targeting signals and post-translational modifications direct it to specific compartments or organelles, influencing its overall activity.
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthesewege und Reaktionsbedingungen
Die Synthese von Ulipristal umfasst mehrere Schritte, beginnend mit 19-NorprogesteronDie Reaktionsbedingungen beinhalten typischerweise die Verwendung von Reagenzien wie Methyllithium oder Methylmagnesiumbromid für die Additionsreaktionen, gefolgt von Hydrolyse- und Kristallisationsschritten zur Reinigung des Endprodukts .
Industrielle Produktionsmethoden
Die industrielle Produktion von Ulipristal beinhaltet die Optimierung des Synthesewegs, um eine hohe Ausbeute und Reinheit zu gewährleisten. Dazu gehört die Kontrolle der Hydrolysebedingungen wie Säuregehalt, Temperatur und Reaktionszeit, um das gewünschte Produkt zu erhalten. Das Endprodukt wird mit Lösungsmitteln wie Ethanol und Isopropanol gereinigt .
Chemische Reaktionsanalyse
Arten von Reaktionen
Ulipristal durchläuft verschiedene chemische Reaktionen, darunter:
Oxidation: Ulipristal kann oxidiert werden, um verschiedene Metaboliten zu bilden.
Reduktion: Reduktionsreaktionen können die in dem Molekül vorhandenen Ketongruppen modifizieren.
Substitution: Substitutionsreaktionen können an der Dimethylaminogruppe oder der Acetoxygruppe auftreten.
Häufige Reagenzien und Bedingungen
Häufige Reagenzien, die bei diesen Reaktionen verwendet werden, sind Oxidationsmittel wie Kaliumpermanganat und Reduktionsmittel wie Natriumborhydrid. Die Reaktionen werden typischerweise unter kontrollierten Temperatur- und pH-Bedingungen durchgeführt, um die gewünschte Produktbildung zu gewährleisten .
Wichtigste gebildete Produkte
Die wichtigsten Produkte, die aus diesen Reaktionen gebildet werden, sind verschiedene Metaboliten, die die Grundstruktur von Ulipristal behalten, aber Modifikationen an bestimmten funktionellen Gruppen aufweisen .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Ulipristal hat eine breite Palette an wissenschaftlichen Forschungsanwendungen:
Chemie: Wird als Modellverbindung verwendet, um selektive Progesteronrezeptor-Modulatoren zu untersuchen.
Biologie: Untersucht nach seinen Wirkungen auf zelluläre Signalwege und Rezeptorbindung.
Medizin: Wird hauptsächlich zur Notfallkontrazeption und zur Behandlung von Uterusmyomen eingesetzt.
Industrie: Wird in der pharmazeutischen Industrie zur Entwicklung von Antibabypillen und Myombehandlungen eingesetzt .
Wirkmechanismus
Ulipristal entfaltet seine Wirkungen durch Bindung an den Progesteronrezeptor, wo es sowohl als Antagonist als auch als partieller Agonist wirkt. Diese Bindung hemmt den Eisprung, indem sie den Follikelsprung verhindert, und kann auch das Endometrium beeinflussen, um eine Embryoimplantation zu verhindern . Die molekularen Zielstrukturen sind der Progesteronrezeptor und in geringerem Maße der Glukokortikoidrezeptor .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Types of Reactions
Ulipristal undergoes various chemical reactions, including:
Oxidation: Ulipristal can be oxidized to form different metabolites.
Reduction: Reduction reactions can modify the ketone groups present in the molecule.
Substitution: Substitution reactions can occur at the dimethylamino group or the acetoxy group.
Common Reagents and Conditions
Common reagents used in these reactions include oxidizing agents like potassium permanganate and reducing agents like sodium borohydride. The reactions are typically carried out under controlled temperature and pH conditions to ensure the desired product formation .
Major Products Formed
The major products formed from these reactions include various metabolites that retain the core structure of ulipristal but with modifications at specific functional groups .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Ähnliche Verbindungen
Mifepriston: Ein weiterer Progesteronrezeptor-Antagonist, der zur medikamentösen Abtreibung und zur Notfallkontrazeption eingesetzt wird.
Levonorgestrel: Ein synthetisches Gestagen, das in der Notfallkontrazeption und in hormonellen Kontrazeptiva verwendet wird.
Einzigartigkeit von Ulipristal
Ulipristal ist einzigartig in seiner dualen Aktivität als sowohl Antagonist als auch partieller Agonist am Progesteronrezeptor, wodurch es ein eindeutiges Wirksamkeits- und Nebenwirkungsprofil im Vergleich zu anderen Verbindungen wie Mifepriston und Levonorgestrel aufweist .
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
(8S,11R,13S,14S,17R)-17-acetyl-11-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]-17-hydroxy-13-methyl-1,2,6,7,8,11,12,14,15,16-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C28H35NO3/c1-17(30)28(32)14-13-25-23-11-7-19-15-21(31)10-12-22(19)26(23)24(16-27(25,28)2)18-5-8-20(9-6-18)29(3)4/h5-6,8-9,15,23-25,32H,7,10-14,16H2,1-4H3/t23-,24+,25-,27-,28-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
HKDLNTKNLJPAIY-WKWWZUSTSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC(=O)C1(CCC2C1(CC(C3=C4CCC(=O)C=C4CCC23)C5=CC=C(C=C5)N(C)C)C)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CC(=O)[C@]1(CC[C@@H]2[C@@]1(C[C@@H](C3=C4CCC(=O)C=C4CC[C@@H]23)C5=CC=C(C=C5)N(C)C)C)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C28H35NO3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID501025842 | |
| Record name | Ulipristal | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID501025842 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
433.6 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
The exact mechanism of action of ulipristal has been heavily debated. On one hand, the majority of official prescribing information labels, monographs, and prior research studies for ulipristal indicated as an emergency contraceptive suggest that its primary mechanism of action revolves around inhibiting or delaying ovulation by suppressing surges in LH that result in the postponement of follicular rupture. Conversely, some of the latest investigations pertaining to ulipristal's mechanism of action as an emergency contraceptive propose that it principally elicits its action by preventing embryo implantation, as opposed to preventing ovulation. Although previous investigations have shown that ulipristal essentially has the ability to prevent ovulation equivalent to placebo (ie. null effect or ability) when administered during LH peaks one to two days before ovulation, the agent still demonstrates a stable and consistently high contraceptive effect of approximately >=80% when used at this time. Subsequently, current studies attempt to investigate how ulipristal could elicit emergency contraception via ovulation prevention under circumstances where ovulation had already clearly been observed. Endometrial biopsy samples studied from such circumstances in such investigations subsequently show that the administered ulipristal causes endometrial tissue to become inhospitable and unsuitable for embryo implantation where a variety of genes characteristic of receptive, pro-gestational endometrium are downregulated. Nevertheless, most if not all proposed mechanisms commonly agree that ulipristal ultimately demonstrates its pharmacological effects by binding to human progesterone receptors and prevents natural, endogenous progesterone from occupying such receptors. Regardless, however, considering current and on-going research into ulipristal's ability to prevent embryo implantation, the notion that the medication can elicit post-fertilization effects potentially raises alerts and/or ethical debates over the use of ulipristal owing to potential abortifacient activity, which is considered to be on par or equipotent to that of mifepristone. Attention should be drawn to the fact that some prescribing information, however, such as the US FDA label for ulipristal indicated for emergency contraception, has included new supplementary commentary since 2018 that directly warns about ulipristal not being indicated for termination of existing pregnancies and suggesting that ulipristal use may confer alterations to the endometrium that may affect implantation and contribute to efficacy. In the treatment of fibroids, ulipristal has been shown to exert direct actions on fibroids reducing their size through inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis. | |
| Record name | Ulipristal | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB08867 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
159811-51-5 | |
| Record name | Ulipristal [USAN:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0159811515 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Ulipristal | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB08867 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Ulipristal | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID501025842 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | (8S,11R,13S,14S,17R)-17-acetyl-11-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]-17-hydroxy-13-methyl-1,2,6,7,8,11,12,14,15,16-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | ULIPRISTAL | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/6J5J15Q2X8 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.


![5-(2,2-Diphenylacetyl)-4-[(4-methoxy-3-methylphenyl)methyl]-1,4,6,7-tetrahydroimidazo[4,5-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid](/img/structure/B1683315.png)
![(7S,9S)-9-acetyl-7-[(2R,4S,5S,6S)-4-[[4-[[[(2S,3S,4S,6R)-6-[[(1S,3S)-3-acetyl-3,5,12-trihydroxy-10-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-2,4-dihydro-1H-tetracen-1-yl]oxy]-3-hydroxy-2-methyloxan-4-yl]amino]methyl]phenyl]methylamino]-5-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-6,9,11-tri](/img/structure/B1683324.png)
![(2S)-2-[[2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-4-amino-2-[[(2R)-3-[2,3-di(hexadecanoyloxy)propylsulfanyl]-2-(hexadecanoylamino)propanoyl]amino]-4-oxobutanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]acetyl]amino]acetyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoic acid](/img/structure/B1683328.png)