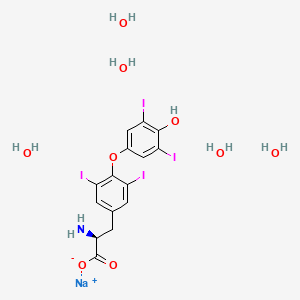
Abacavir
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Abacavir is a synthetic carbocyclic nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitor used primarily in the treatment of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS). It is marketed under the brand name Ziagen among others. This compound is typically used in combination with other antiretroviral medications and is not recommended for use alone . It is known for its ability to inhibit the replication of HIV by targeting the reverse transcriptase enzyme, which is crucial for the virus’s replication process .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Abacavir hat eine breite Palette von Anwendungen in der wissenschaftlichen Forschung, insbesondere in den Bereichen Chemie, Biologie und Medizin:
Chemie: this compound dient als Modellverbindung zur Untersuchung von Nukleosidanaloga und deren Wechselwirkungen mit Enzymen.
Biologie: Es wird verwendet, um die Mechanismen der viralen Replikation und die Entwicklung von Resistenzen bei HIV zu untersuchen.
Medizin: this compound ist ein wichtiger Bestandteil der antiretroviralen Therapie bei HIV/AIDS.
5. Wirkmechanismus
This compound wird intrazellulär zu seinem aktiven Metaboliten, Carbovirtriphosphat, umgewandelt. Dieser Metabolit ist ein Analog von Desoxyguanosin-5'-triphosphat (dGTP) und konkurriert mit dem HIV-Reverse-Transkriptase-Enzym um die Einlagerung in die virale DNA. Nach der Einlagerung wirkt es als Kettenterminator, der die Elongation der viralen DNA verhindert und so die Replikation des Virus hemmt .
Ähnliche Verbindungen:
Lamivudin: Ein weiterer Nukleosid-Reverse-Transkriptase-Hemmer, der in Kombination mit this compound eingesetzt wird.
Zidovudin: Ein älterer Nukleosid-Reverse-Transkriptase-Hemmer mit einem ähnlichen Wirkmechanismus.
Tenofovir: Ein Nukleotid-Reverse-Transkriptase-Hemmer mit einer anderen chemischen Struktur, aber ähnlicher antiviraler Aktivität.
Vergleich:
Eindeutigkeit: this compound ist einzigartig in seiner Struktur als carbocyclisches Nukleosidanalogon. Es hat eine charakteristische Cyclopropylamin-Gruppe, die es von anderen Nukleosidanaloga unterscheidet.
Sicherheitsprofil: This compound hat ein gut dokumentiertes Sicherheitsprofil, obwohl es mit einem Risiko für Überempfindlichkeitsreaktionen und potenziellen kardiovaskulären Risiken verbunden ist.
Wirkmechanismus
Target of Action
Abacavir is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI) with activity against Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 (HIV-1) . The primary target of this compound is the HIV-1 reverse transcriptase enzyme . This enzyme is crucial for the replication of the HIV virus, as it is responsible for the transcription of viral RNA into DNA .
Mode of Action
This compound is converted by cellular enzymes to the active metabolite carbovir triphosphate, an analogue of deoxyguanosine-5’-triphosphate (dGTP) . This active metabolite competes with natural nucleotides for incorporation into the viral DNA . When incorporated, it inhibits the HIV reverse transcriptase enzyme competitively and acts as a chain terminator of DNA synthesis . This prevents the virus from replicating and reduces the viral load in the body .
Biochemical Pathways
This compound interferes with the reverse transcription process, a critical step in the HIV life cycle . By inhibiting the reverse transcriptase enzyme, it prevents the conversion of viral RNA into DNA, thus blocking the integration of viral DNA into the host genome . This ultimately leads to a decrease in viral replication and an increase in CD4 cell counts .
Pharmacokinetics
This compound is rapidly absorbed following oral administration, with a mean absolute bioavailability of approximately 83% . Maximum this compound concentrations are observed in serum within 0.5 to 3.0 hours of dosing in the fasted state (median Tmax of 1 - 1.5 hour) . The elimination half-life of this compound is 1.5 hours . It is primarily metabolized through cytosolic alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) enzymes .
Action Environment
The efficacy and stability of this compound can be influenced by various environmental factors. For instance, genetic factors can play a significant role. The presence of the HLA-B*57:01 allele is strongly linked to the occurrence of a hypersensitivity reaction to this compound . Therefore, testing for this allele prior to this compound treatment is recommended . Additionally, drug interactions can also influence the action of this compound. Since this compound is primarily metabolized by ADH and UGT enzymes, no interactions between this compound and inducers or inhibitors of cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes are predicted .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthesewege und Reaktionsbedingungen: Die Synthese von Abacavir umfasst mehrere Schritte, beginnend mit einer geeigneten Dihaloaminopyrimidin-Verbindung. Die wichtigsten Schritte sind:
Reaktion mit Aminoalkohol: Das Dihaloaminopyrimidin wird mit einem Aminoalkohol umgesetzt, um eine Zwischenverbindung zu bilden.
Cyclisierung: Diese Zwischenverbindung wird cyclisiert, um eine Schlüsselzwischenverbindung zu bilden.
Einführung von Cyclopropylamin: Das Chloratom in der Zwischenverbindung wird durch Cyclopropylamin substituiert, um this compound als freie Base zu erhalten.
Industrielle Produktionsverfahren: Die industrielle Produktion von this compound beinhaltet oft die Optimierung der Reaktionsbedingungen, um eine hohe Ausbeute und Reinheit zu gewährleisten. Dazu gehören die Kontrolle der Temperatur, des pH-Werts und der Verwendung spezifischer Katalysatoren, um die Reaktionen zu erleichtern. Der Prozess kann auch Reinigungsschritte wie Kristallisation und Chromatographie umfassen, um das Endprodukt zu isolieren .
Arten von Reaktionen:
Oxidation: this compound unterliegt einem oxidativen Abbau, der mit elektrochemischen Methoden untersucht werden kann.
Reduktion: Obwohl spezifische Reduktionsreaktionen von this compound weniger gut dokumentiert sind, ist es möglich, dass this compound unter bestimmten Bedingungen einer Reduktion unterliegen könnte.
Substitution: Die Synthese von this compound selbst beinhaltet Substitutionsreaktionen, insbesondere die Substitution von Chlor durch Cyclopropylamin.
Häufige Reagenzien und Bedingungen:
Oxidation: Wasserstoffperoxid, Platinelektroden, bor-dotierte Diamantelektroden.
Substitution: Cyclopropylamin, verschiedene Lösungsmittel und Katalysatoren.
Hauptprodukte:
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Lamivudine: Another nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor used in combination with abacavir.
Zidovudine: An older nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor with a similar mechanism of action.
Tenofovir: A nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor with a different chemical structure but similar antiviral activity.
Comparison:
Uniqueness: this compound is unique in its structure as a carbocyclic nucleoside analog. It has a distinct cyclopropylamine group that differentiates it from other nucleoside analogs.
Safety Profile: this compound has a well-documented safety profile, though it is associated with a risk of hypersensitivity reactions and potential cardiovascular risks.
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
[4-[2-amino-6-(cyclopropylamino)purin-9-yl]cyclopent-2-en-1-yl]methanol | |
|---|---|---|
| Details | Computed by Lexichem TK 2.7.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C14H18N6O/c15-14-18-12(17-9-2-3-9)11-13(19-14)20(7-16-11)10-4-1-8(5-10)6-21/h1,4,7-10,21H,2-3,5-6H2,(H3,15,17,18,19) | |
| Details | Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
MCGSCOLBFJQGHM-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Details | Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1CC1NC2=C3C(=NC(=N2)N)N(C=N3)C4CC(C=C4)CO | |
| Details | Computed by OEChem 2.3.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C14H18N6O | |
| Details | Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID20861337 | |
| Record name | 4-[2-Amino-6-(cyclopropylamino)-9H-purin-9-yl]-2-cyclopentene-1-methanol | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID20861337 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
286.33 g/mol | |
| Details | Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
CAS No. |
136470-78-5, 914348-29-1 | |
| Record name | NSC742406 | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=742406 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | 4-[2-Amino-6-(cyclopropylamino)-9H-purin-9-yl]-2-cyclopentene-1-methanol | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID20861337 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.


![ethyl (2S)-2-[[2-(acetylsulfanylmethyl)-3-(2-methylphenyl)propanoyl]amino]-4-methylsulfanylbutanoate](/img/structure/B1662769.png)
![10-methyl-7-[(5-methyl-1H-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]-8,9-dihydro-7H-pyrido[1,2-a]indol-6-one;hydrochloride](/img/structure/B1662777.png)
![1-(7-(4-Fluorophenyl)-8-(pyridin-4-yl)-3,4-dihydropyrazolo[5,1-c][1,2,4]triazin-2(1H)-yl)-2-phenylethane-1,2-dione sulfate](/img/structure/B1662783.png)