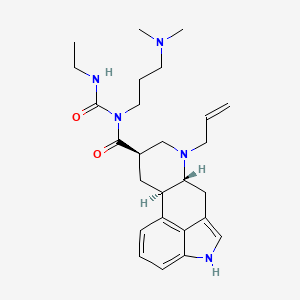
Cabergolin
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Cabergolin ist ein dopaminerges Medikament, das hauptsächlich zur Behandlung von Erkrankungen eingesetzt wird, die mit hohen Prolaktinspiegeln verbunden sind, wie z. B. Prolactinomen und Hyperprolaktinämie. Es wird auch bei der Behandlung der Parkinson-Krankheit und anderer Erkrankungen eingesetzt. This compound ist ein Ergotaminderivat und wirkt als potenter Agonist des Dopamin-D2-Rezeptors .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Cabergolin hat eine breite Palette an Anwendungen in der wissenschaftlichen Forschung:
Medizin: Es wird zur Behandlung von hyperprolaktinämischen Störungen, Parkinson-Krankheit und prolaktinsekretierenden Hypophysenadenomen eingesetzt.
Wirkmechanismus
This compound entfaltet seine Wirkung, indem es die Dopamin-D2-Rezeptoren stimuliert, die G-Protein-gekoppelte Rezeptoren sind, die mit Gi-Proteinen assoziiert sind. In Laktrotrophen hemmt die Stimulation von Dopamin-D2-Rezeptoren die Adenylylcyclase, wodurch die intrazelluläre Konzentration von cyclischem Adenosinmonophosphat (cAMP) verringert und die IP3-abhängige Freisetzung von Kalzium aus intrazellulären Speichern blockiert wird. Dies führt zur Hemmung der Prolaktinsekretion .
Wirkmechanismus
Target of Action
Cabergoline is a long-acting dopamine agonist and prolactin inhibitor . It primarily targets the dopamine D2 receptors , which are mainly found in the anterior pituitary and the nigrostriatal pathway . These receptors play a crucial role in the regulation of prolactin secretion and coordinated muscle activity .
Mode of Action
Cabergoline interacts with its targets by binding to the dopamine D2 receptors . This binding causes inhibition of adenylyl cyclase, which decreases intracellular cAMP concentrations and blocks IP3-dependent release of Ca2+ from intracellular stores . This interaction results in the suppression of prolactin secretion from lactotrophs of the anterior pituitary .
Biochemical Pathways
The primary biochemical pathway affected by cabergoline is the dopamine signaling pathway. By binding to the dopamine D2 receptors, cabergoline inhibits the activity of adenylyl cyclase, leading to a decrease in cAMP levels . This decrease in cAMP levels then inhibits the release of prolactin, thereby suppressing prolactin secretion .
Pharmacokinetics
Cabergoline exhibits linear pharmacokinetics over a dose range of 0.5–7mg in healthy adult volunteers and parkinsonian patients . It is moderately bound (around 40%) to human plasma proteins in a concentration-independent manner . The absolute bioavailability of cabergoline is unknown . It is extensively metabolized by the liver, predominantly via hydrolysis of the acylurea bond of the urea moiety . Less than 4% is excreted unchanged in the urine . The elimination half-life of cabergoline estimated from urinary data of healthy subjects ranges between 63 and 109 hours .
Result of Action
The molecular and cellular effects of cabergoline’s action primarily involve the suppression of prolactin secretion from lactotrophs of the anterior pituitary . Recent studies have also revealed that cabergoline suppresses tumor cell proliferation and induces cell death .
Biochemische Analyse
Biochemical Properties
Cabergoline interacts with dopamine D2 receptors, exhibiting potent agonist activity . It is extensively metabolized by the liver, predominantly via hydrolysis of the acylurea bond of the urea moiety . Cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism is minimal .
Cellular Effects
Cabergoline has been shown to influence various types of cells and cellular processes. It is used to reduce the production of a hormone called prolactin by the pituitary gland . In human endometrial stromal cells, Cabergoline treatment more than doubled decidual biomarker expression . It also induced characteristic decidual morphology changes and blocked detrimental effects of IL-1β on decidual cytology .
Molecular Mechanism
Cabergoline exerts its effects at the molecular level primarily through its action as a dopamine D2 receptor agonist . The stimulation of dopamine D2 receptors leads to improvements in coordinated muscle activity in those with movement disorders .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
Cabergoline is a long-acting medication, usually taken once or twice a week . The elimination half-life of cabergoline estimated from urinary data of healthy subjects ranges between 63 and 109 hours .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of Cabergoline can vary with different dosages in animal models
Metabolic Pathways
Cabergoline is involved in metabolic pathways predominantly via hydrolysis of the acylurea bond of the urea moiety . The major metabolites identified thus far do not contribute to the therapeutic effect of Cabergoline .
Subcellular Localization
In terms of subcellular localization, one study found strong immunohistochemistry localization of dopamine D2 receptors (which Cabergoline interacts with) in the endometrial stromal compartment with a subcellular distribution distinct from that of ERα .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Cabergolin wird aus Ergo-8β-Carbonsäureester durch eine Reihe chemischer Reaktionen synthetisiert. Der Prozess beinhaltet die Schutz der sekundären Amin- und der Indol-Stickstoff-Funktionen von Ergo-8β-Carbonsäure C1-4 Alkyl-Estern als Carbamat-Derivate. Die geschützte Verbindung wird dann mit 3-(Dimethylamino)propylamin amidiert, mit Ethylisocyanat umgesetzt, und die Schutzgruppen werden abgespalten. Schließlich wird das entschützte sekundäre Amin mit einem elektrophilen Allylalkohol-Derivat umgesetzt, um this compound zu erhalten .
Chemische Reaktionsanalyse
This compound unterliegt verschiedenen chemischen Reaktionen, darunter Hydrolyse und Oxidation. Es ist sehr empfindlich gegenüber Hydrolyse, insbesondere an der Harnstoffgruppe und der Amidgruppe. Die Alkenbindung in this compound ist anfällig für Oxidation. Übliche Reagenzien, die bei diesen Reaktionen verwendet werden, sind Wasser für die Hydrolyse und Oxidationsmittel für die Oxidation. Die Hauptprodukte, die aus diesen Reaktionen gebildet werden, sind Abbauprodukte, die mittels Infrarot- und Massenspektroskopie analysiert wurden.
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Cabergoline undergoes various chemical reactions, including hydrolysis and oxidation. It is highly sensitive to hydrolysis, particularly at the urea moiety and amide group. The alkene bond in cabergoline is susceptible to oxidation. Common reagents used in these reactions include water for hydrolysis and oxidizing agents for oxidation. The major products formed from these reactions are degradation products identified using infrared and mass spectrometry analyses.
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Cabergolin wird oft mit anderen Dopaminagonisten wie Bromocriptin und Pergolid verglichen. Während alle drei Verbindungen zur Behandlung von Hyperprolaktinämie und Parkinson-Krankheit eingesetzt werden, hat this compound eine längere Halbwertszeit und eine höhere Affinität zu Dopamin-D2-Rezeptoren, wodurch es wirksamer und von Patienten besser vertragen wird . Bromocriptin und Pergolid haben kürzere Halbwertszeiten und können eine häufigere Dosierung erfordern .
Ähnliche Verbindungen
- Bromocriptin
- Pergolid
- Quinagolid
Die einzigartigen Eigenschaften von this compound, wie z. B. seine lange Halbwertszeit und seine hohe Rezeptoraffinität, machen es für viele Patienten und Gesundheitsdienstleister zur bevorzugten Wahl.
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
(6aR,9R,10aR)-N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-N-(ethylcarbamoyl)-7-prop-2-enyl-6,6a,8,9,10,10a-hexahydro-4H-indolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C26H37N5O2/c1-5-11-30-17-19(25(32)31(26(33)27-6-2)13-8-12-29(3)4)14-21-20-9-7-10-22-24(20)18(16-28-22)15-23(21)30/h5,7,9-10,16,19,21,23,28H,1,6,8,11-15,17H2,2-4H3,(H,27,33)/t19-,21-,23-/m1/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
KORNTPPJEAJQIU-KJXAQDMKSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CCNC(=O)N(CCCN(C)C)C(=O)C1CC2C(CC3=CNC4=CC=CC2=C34)N(C1)CC=C | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CCNC(=O)N(CCCN(C)C)C(=O)[C@@H]1C[C@H]2[C@@H](CC3=CNC4=CC=CC2=C34)N(C1)CC=C | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C26H37N5O2 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
85329-89-1 (diphosphate) | |
| Record name | Cabergoline [USAN:USP:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0081409907 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID6022719 | |
| Record name | Cabergoline | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID6022719 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
451.6 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Cabergoline | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014393 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
Insoluble, 6.40e-02 g/L | |
| Record name | Cabergoline | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00248 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Cabergoline | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014393 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
The dopamine D2 receptor is a 7-transmembrane G-protein coupled receptor associated with Gi proteins. In lactotrophs, stimulation of dopamine D2 causes inhibition of adenylyl cyclase, which decreases intracellular cAMP concentrations and blocks IP3-dependent release of Ca2+ from intracellular stores. Decreases in intracellular calcium levels may also be brought about via inhibition of calcium influx through voltage-gated calcium channels, rather than via inhibition of adenylyl cyclase. Additionally, receptor activation blocks phosphorylation of p42/p44 MAPK and decreases MAPK/ERK kinase phosphorylation. Inhibition of MAPK appears to be mediated by c-Raf and B-Raf-dependent inhibition of MAPK/ERK kinase. Dopamine-stimulated growth hormone release from the pituitary gland is mediated by a decrease in intracellular calcium influx through voltage-gated calcium channels rather than via adenylyl cyclase inhibition. Stimulation of dopamine D2 receptors in the nigrostriatal pathway leads to improvements in coordinated muscle activity in those with movement disorders. Cabergoline is a long-acting dopamine receptor agonist with a high affinity for D2 receptors. Receptor-binding studies indicate that cabergoline has low affinity for dopamine D1, α1,- and α2- adrenergic, and 5-HT1- and 5-HT2-serotonin receptors. | |
| Record name | Cabergoline | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00248 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
81409-90-7 | |
| Record name | Cabergoline | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=81409-90-7 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Cabergoline [USAN:USP:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0081409907 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Cabergoline | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00248 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Cabergoline | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID6022719 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | (6aR,9R,10aR)-N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-N-(ethylcarbamoyl)-7-prop-2-enyl-6,6a,8,9,10,10a-hexahydro-4H-indolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | CABERGOLINE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/LL60K9J05T | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Cabergoline | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014393 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
102-104 °C, 102 - 104 °C | |
| Record name | Cabergoline | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00248 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Cabergoline | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014393 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Q1: What is the primary mechanism of action of Cabergoline?
A: Cabergoline exerts its therapeutic effect primarily by acting as a dopamine receptor agonist, exhibiting a high affinity for the dopamine D2 receptor subtype. [, , ] This interaction mimics the action of dopamine, a neurotransmitter, leading to a cascade of downstream effects.
Q2: How does Cabergoline's interaction with dopamine D2 receptors affect prolactin secretion?
A: Prolactin secretion from the pituitary gland is under tonic inhibitory control by dopamine. By binding to D2 receptors on lactotroph cells in the pituitary gland, Cabergoline inhibits the synthesis and release of prolactin. [, , , ]
Q3: Beyond prolactin, what other hormonal or physiological processes are influenced by Cabergoline?
A: Cabergoline's action on dopamine receptors extends beyond prolactin regulation. It can also affect growth hormone secretion, potentially finding application in managing acromegaly. [, , ] Additionally, its influence on the dopaminergic system suggests potential applications in treating conditions like Parkinson's disease. [, , , ]
Q4: What is the molecular formula and weight of Cabergoline?
A: Cabergoline is represented by the molecular formula C26H37N5O2 and has a molecular weight of 451.6 g/mol. []
Q5: Is there any available spectroscopic data for Cabergoline?
A: While the provided research doesn't delve into specific spectroscopic data, techniques like nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and mass spectrometry (MS) are commonly employed for the structural characterization of compounds like Cabergoline. []
Q6: Is there information available regarding the material compatibility and stability of Cabergoline under various conditions?
A6: The provided research focuses primarily on Cabergoline's pharmacological properties and applications in biological systems. Specific details regarding its material compatibility and stability in non-biological contexts are not discussed.
Q7: Are there any known factors that influence the pharmacokinetics of Cabergoline?
A: Concomitant administration of drugs like clarithromycin, a potent inhibitor of CYP3A4 (a key enzyme involved in drug metabolism), can significantly increase the blood concentration of Cabergoline. []
Q8: What are the primary clinical applications of Cabergoline?
A: Cabergoline is primarily prescribed for the treatment of hyperprolactinemia, often caused by prolactinomas. [, , , , ] Its efficacy in normalizing prolactin levels, restoring ovulation and fertility in women, and reducing tumor size has been well-documented. [, , , , ]
Q9: Can Cabergoline be used during pregnancy?
A: While the use of Cabergoline during pregnancy has been reported, and available data suggests it may be relatively safe, bromocriptine, another dopamine agonist, has a larger safety database and a more established safety record for use during pregnancy. []
Q10: Is Cabergoline effective in treating conditions other than hyperprolactinemia?
A: Emerging research suggests potential applications for Cabergoline in managing acromegaly, either as monotherapy or in combination with other drugs like pegvisomant. [, , ] Additionally, its use in treating Parkinson's disease and restless legs syndrome has been explored. [, , , ]
Q11: Are there alternative treatment options for individuals with Cabergoline-resistant prolactinomas?
A: In cases of Cabergoline resistance, alternative dopamine agonists like bromocriptine might be considered, although they often have a less favorable side-effect profile. [] Other options include surgery or radiotherapy. [, ]
Q12: Are there any specific drug delivery or targeting strategies being explored for Cabergoline?
A12: The provided research primarily focuses on Cabergoline's systemic effects. Targeted drug delivery strategies are not extensively discussed within this context.
Q13: What analytical methods are commonly used to characterize and quantify Cabergoline?
A: Techniques like high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) coupled with mass spectrometry (MS) are commonly employed to analyze Cabergoline and its metabolites. []
Q14: Is there information available on the environmental impact and degradation of Cabergoline?
A14: The provided research primarily focuses on the pharmacological aspects of Cabergoline in treating human conditions. Environmental impact and degradation are not discussed within this scope.
Q15: Are there any cross-disciplinary applications or research synergies related to Cabergoline?
A: Research on Cabergoline spans various disciplines, including endocrinology, neurology, and pharmacology. Its mechanisms of action and effects on hormone regulation have implications for understanding pituitary gland function and dopamine signaling pathways. [, , , , , , , , , , , , , , ]
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.


![[3-(2,2-dimethylbutanoylamino)phenyl] N-methylcarbamate](/img/structure/B1668131.png)