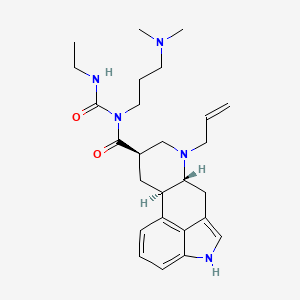
Cabergolina
Descripción general
Descripción
La cabergolina es un medicamento dopaminérgico que se utiliza principalmente para tratar afecciones asociadas con altos niveles de prolactina, como prolactinomas e hiperprolactinemia. También se utiliza en el manejo de la enfermedad de Parkinson y otros trastornos. La this compound es un derivado del cornezuelo de centeno y actúa como un potente agonista del receptor de dopamina D2 .
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
Cabergoline has a wide range of scientific research applications:
Medicine: It is used to treat hyperprolactinemic disorders, Parkinson’s disease, and prolactin-secreting pituitary adenomas.
Endocrinology: It is effective in managing conditions like acromegaly and Cushing’s disease by suppressing hormone production and inducing tumor shrinkage.
Mecanismo De Acción
La cabergolina ejerce sus efectos estimulando los receptores de dopamina D2, que son receptores acoplados a proteínas G asociados con proteínas Gi. En los lactotropos, la estimulación de los receptores de dopamina D2 inhibe la adenilato ciclasa, lo que disminuye las concentraciones intracelulares de monofosfato de adenosina cíclico (AMPc) y bloquea la liberación de calcio de las reservas intracelulares dependiente de trifosfato de inositol (IP3). Esto da como resultado la inhibición de la secreción de prolactina .
Análisis Bioquímico
Biochemical Properties
Cabergoline interacts with dopamine D2 receptors, exhibiting potent agonist activity . It is extensively metabolized by the liver, predominantly via hydrolysis of the acylurea bond of the urea moiety . Cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism is minimal .
Cellular Effects
Cabergoline has been shown to influence various types of cells and cellular processes. It is used to reduce the production of a hormone called prolactin by the pituitary gland . In human endometrial stromal cells, Cabergoline treatment more than doubled decidual biomarker expression . It also induced characteristic decidual morphology changes and blocked detrimental effects of IL-1β on decidual cytology .
Molecular Mechanism
Cabergoline exerts its effects at the molecular level primarily through its action as a dopamine D2 receptor agonist . The stimulation of dopamine D2 receptors leads to improvements in coordinated muscle activity in those with movement disorders .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
Cabergoline is a long-acting medication, usually taken once or twice a week . The elimination half-life of cabergoline estimated from urinary data of healthy subjects ranges between 63 and 109 hours .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of Cabergoline can vary with different dosages in animal models
Metabolic Pathways
Cabergoline is involved in metabolic pathways predominantly via hydrolysis of the acylurea bond of the urea moiety . The major metabolites identified thus far do not contribute to the therapeutic effect of Cabergoline .
Subcellular Localization
In terms of subcellular localization, one study found strong immunohistochemistry localization of dopamine D2 receptors (which Cabergoline interacts with) in the endometrial stromal compartment with a subcellular distribution distinct from that of ERα .
Métodos De Preparación
La cabergolina se sintetiza a partir del éster de ácido ergolina-8β-carboxílico a través de una serie de reacciones químicas. El proceso implica la protección de las funciones de amina secundaria y nitrógeno indólico del éster alquílico C1-4 del ácido ergolina-8β-carboxílico como derivados de carbamato. El compuesto protegido se amida entonces con 3-(dimetilamino)propilamina, reacciona con isocianato de etilo y los grupos protectores se escinden. Finalmente, la amina secundaria desprotegida se hace reaccionar con un derivado de alcohol alílico electrófilo para obtener this compound .
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
La cabergolina experimenta diversas reacciones químicas, como la hidrólisis y la oxidación. Es muy sensible a la hidrólisis, especialmente en la parte de la urea y el grupo amida. El enlace alqueno de la this compound es susceptible a la oxidación. Los reactivos comunes utilizados en estas reacciones incluyen el agua para la hidrólisis y los agentes oxidantes para la oxidación. Los principales productos formados a partir de estas reacciones son productos de degradación que se identifican mediante análisis de espectrometría de infrarrojos y de masas.
Aplicaciones en Investigación Científica
La this compound tiene una amplia gama de aplicaciones en investigación científica:
Medicina: Se utiliza para tratar trastornos hiperprolactinémicos, la enfermedad de Parkinson y los adenomas hipofisarios que secretan prolactina.
Endocrinología: Es eficaz en el manejo de afecciones como la acromegalia y la enfermedad de Cushing al suprimir la producción hormonal e inducir la reducción del tumor.
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
La cabergolina se suele comparar con otros agonistas de la dopamina como la bromocriptina y la pergolida. Aunque los tres compuestos se utilizan para tratar la hiperprolactinemia y la enfermedad de Parkinson, la this compound tiene una vida media más larga y una mayor afinidad por los receptores de dopamina D2, lo que la hace más eficaz y mejor tolerada por los pacientes . La bromocriptina y la pergolida tienen vidas medias más cortas y pueden requerir una dosificación más frecuente .
Compuestos similares
- Bromocriptina
- Pergolida
- Quinagolida
Las propiedades únicas de la this compound, como su larga vida media y su alta afinidad por los receptores, la convierten en una opción preferida para muchos pacientes y proveedores de atención médica.
Propiedades
IUPAC Name |
(6aR,9R,10aR)-N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-N-(ethylcarbamoyl)-7-prop-2-enyl-6,6a,8,9,10,10a-hexahydro-4H-indolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C26H37N5O2/c1-5-11-30-17-19(25(32)31(26(33)27-6-2)13-8-12-29(3)4)14-21-20-9-7-10-22-24(20)18(16-28-22)15-23(21)30/h5,7,9-10,16,19,21,23,28H,1,6,8,11-15,17H2,2-4H3,(H,27,33)/t19-,21-,23-/m1/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
KORNTPPJEAJQIU-KJXAQDMKSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CCNC(=O)N(CCCN(C)C)C(=O)C1CC2C(CC3=CNC4=CC=CC2=C34)N(C1)CC=C | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CCNC(=O)N(CCCN(C)C)C(=O)[C@@H]1C[C@H]2[C@@H](CC3=CNC4=CC=CC2=C34)N(C1)CC=C | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C26H37N5O2 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
85329-89-1 (diphosphate) | |
| Record name | Cabergoline [USAN:USP:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0081409907 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID6022719 | |
| Record name | Cabergoline | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID6022719 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
451.6 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Cabergoline | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014393 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
Insoluble, 6.40e-02 g/L | |
| Record name | Cabergoline | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00248 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Cabergoline | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014393 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
The dopamine D2 receptor is a 7-transmembrane G-protein coupled receptor associated with Gi proteins. In lactotrophs, stimulation of dopamine D2 causes inhibition of adenylyl cyclase, which decreases intracellular cAMP concentrations and blocks IP3-dependent release of Ca2+ from intracellular stores. Decreases in intracellular calcium levels may also be brought about via inhibition of calcium influx through voltage-gated calcium channels, rather than via inhibition of adenylyl cyclase. Additionally, receptor activation blocks phosphorylation of p42/p44 MAPK and decreases MAPK/ERK kinase phosphorylation. Inhibition of MAPK appears to be mediated by c-Raf and B-Raf-dependent inhibition of MAPK/ERK kinase. Dopamine-stimulated growth hormone release from the pituitary gland is mediated by a decrease in intracellular calcium influx through voltage-gated calcium channels rather than via adenylyl cyclase inhibition. Stimulation of dopamine D2 receptors in the nigrostriatal pathway leads to improvements in coordinated muscle activity in those with movement disorders. Cabergoline is a long-acting dopamine receptor agonist with a high affinity for D2 receptors. Receptor-binding studies indicate that cabergoline has low affinity for dopamine D1, α1,- and α2- adrenergic, and 5-HT1- and 5-HT2-serotonin receptors. | |
| Record name | Cabergoline | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00248 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
81409-90-7 | |
| Record name | Cabergoline | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=81409-90-7 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Cabergoline [USAN:USP:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0081409907 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Cabergoline | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00248 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Cabergoline | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID6022719 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | (6aR,9R,10aR)-N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-N-(ethylcarbamoyl)-7-prop-2-enyl-6,6a,8,9,10,10a-hexahydro-4H-indolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | CABERGOLINE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/LL60K9J05T | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Cabergoline | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014393 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
102-104 °C, 102 - 104 °C | |
| Record name | Cabergoline | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00248 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Cabergoline | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014393 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Q1: What is the primary mechanism of action of Cabergoline?
A: Cabergoline exerts its therapeutic effect primarily by acting as a dopamine receptor agonist, exhibiting a high affinity for the dopamine D2 receptor subtype. [, , ] This interaction mimics the action of dopamine, a neurotransmitter, leading to a cascade of downstream effects.
Q2: How does Cabergoline's interaction with dopamine D2 receptors affect prolactin secretion?
A: Prolactin secretion from the pituitary gland is under tonic inhibitory control by dopamine. By binding to D2 receptors on lactotroph cells in the pituitary gland, Cabergoline inhibits the synthesis and release of prolactin. [, , , ]
Q3: Beyond prolactin, what other hormonal or physiological processes are influenced by Cabergoline?
A: Cabergoline's action on dopamine receptors extends beyond prolactin regulation. It can also affect growth hormone secretion, potentially finding application in managing acromegaly. [, , ] Additionally, its influence on the dopaminergic system suggests potential applications in treating conditions like Parkinson's disease. [, , , ]
Q4: What is the molecular formula and weight of Cabergoline?
A: Cabergoline is represented by the molecular formula C26H37N5O2 and has a molecular weight of 451.6 g/mol. []
Q5: Is there any available spectroscopic data for Cabergoline?
A: While the provided research doesn't delve into specific spectroscopic data, techniques like nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and mass spectrometry (MS) are commonly employed for the structural characterization of compounds like Cabergoline. []
Q6: Is there information available regarding the material compatibility and stability of Cabergoline under various conditions?
A6: The provided research focuses primarily on Cabergoline's pharmacological properties and applications in biological systems. Specific details regarding its material compatibility and stability in non-biological contexts are not discussed.
Q7: Are there any known factors that influence the pharmacokinetics of Cabergoline?
A: Concomitant administration of drugs like clarithromycin, a potent inhibitor of CYP3A4 (a key enzyme involved in drug metabolism), can significantly increase the blood concentration of Cabergoline. []
Q8: What are the primary clinical applications of Cabergoline?
A: Cabergoline is primarily prescribed for the treatment of hyperprolactinemia, often caused by prolactinomas. [, , , , ] Its efficacy in normalizing prolactin levels, restoring ovulation and fertility in women, and reducing tumor size has been well-documented. [, , , , ]
Q9: Can Cabergoline be used during pregnancy?
A: While the use of Cabergoline during pregnancy has been reported, and available data suggests it may be relatively safe, bromocriptine, another dopamine agonist, has a larger safety database and a more established safety record for use during pregnancy. []
Q10: Is Cabergoline effective in treating conditions other than hyperprolactinemia?
A: Emerging research suggests potential applications for Cabergoline in managing acromegaly, either as monotherapy or in combination with other drugs like pegvisomant. [, , ] Additionally, its use in treating Parkinson's disease and restless legs syndrome has been explored. [, , , ]
Q11: Are there alternative treatment options for individuals with Cabergoline-resistant prolactinomas?
A: In cases of Cabergoline resistance, alternative dopamine agonists like bromocriptine might be considered, although they often have a less favorable side-effect profile. [] Other options include surgery or radiotherapy. [, ]
Q12: Are there any specific drug delivery or targeting strategies being explored for Cabergoline?
A12: The provided research primarily focuses on Cabergoline's systemic effects. Targeted drug delivery strategies are not extensively discussed within this context.
Q13: What analytical methods are commonly used to characterize and quantify Cabergoline?
A: Techniques like high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) coupled with mass spectrometry (MS) are commonly employed to analyze Cabergoline and its metabolites. []
Q14: Is there information available on the environmental impact and degradation of Cabergoline?
A14: The provided research primarily focuses on the pharmacological aspects of Cabergoline in treating human conditions. Environmental impact and degradation are not discussed within this scope.
Q15: Are there any cross-disciplinary applications or research synergies related to Cabergoline?
A: Research on Cabergoline spans various disciplines, including endocrinology, neurology, and pharmacology. Its mechanisms of action and effects on hormone regulation have implications for understanding pituitary gland function and dopamine signaling pathways. [, , , , , , , , , , , , , , ]
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.


![[3-(2,2-dimethylbutanoylamino)phenyl] N-methylcarbamate](/img/structure/B1668131.png)