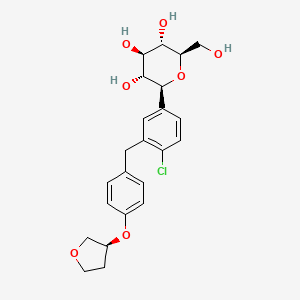
Empagliflozine
Vue d'ensemble
Description
L'empagliflozine est un médicament oral utilisé principalement pour gérer le diabète de type 2. Il appartient à la classe des médicaments appelés inhibiteurs du cotransporteur sodium-glucose 2 (SGLT2). En inhibant le SGLT2, l'this compound réduit la réabsorption du glucose dans les reins, ce qui entraîne une augmentation de l'excrétion du glucose dans les urines. Cela aide à abaisser le taux de sucre dans le sang chez les patients atteints de diabète de type 2 .
Applications De Recherche Scientifique
Empagliflozin has a wide range of scientific research applications, including:
Diabetes Management: Empagliflozin is primarily used to manage type 2 diabetes by lowering blood sugar levels
Cardiovascular Benefits: Research has shown that empagliflozin can reduce the risk of cardiovascular events, such as heart attacks and strokes, in patients with type 2 diabetes
Renal Protection: Empagliflozin has been found to have nephroprotective effects, reducing the risk of kidney disease progression.
Heart Failure: The compound is also used to treat heart failure, providing benefits beyond glucose control.
Mécanisme D'action
Target of Action
Empagliflozin primarily targets the sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) . SGLT2 is the predominant transporter responsible for the reabsorption of glucose from the glomerular filtrate back into the circulation . It is primarily located in the kidney and plays a crucial role in maintaining glucose homeostasis .
Mode of Action
Empagliflozin acts as an inhibitor of SGLT2 . By inhibiting SGLT2, empagliflozin prevents glucose reabsorption in the kidneys, thereby increasing the amount of glucose excreted in the urine . This leads to a reduction in blood glucose levels, which is beneficial for managing type 2 diabetes mellitus .
Biochemical Pathways
Empagliflozin’s action on SGLT2 affects several biochemical pathways. One of the key pathways involves the NLRP3 inflammasome and MyD88-related pathways . Inhibition of these pathways by empagliflozin has been associated with anti-apoptotic and anti-fibrotic effects . Additionally, empagliflozin has been shown to impact pathways related to cardiomyocyte contraction/relaxation, iron handling, and other metabolic and renal targets .
Result of Action
Empagliflozin has several molecular and cellular effects. It has been shown to ameliorate myocardial extracellular matrix remodeling, cardiomyocyte stiffness, and concentric hypertrophy . Additionally, empagliflozin has been found to inhibit microglia activation and neuroinflammation resulting from injury . It also improves pancreatic beta-cell function by reducing pancreatic beta-cell burden and glucotoxicity .
Action Environment
The action of empagliflozin can be influenced by various environmental factors. For instance, renal function can impact the efficacy of empagliflozin, as its mechanism of action is contingent on the renal excretion of glucose . Therefore, empagliflozin may be held in cases of acute kidney injury . Furthermore, the drug’s blood pressure-lowering effects have been associated with its action in non-diabetic hypertensive rats .
Méthodes De Préparation
Voies de synthèse et conditions de réaction : L'empagliflozine est synthétisée par un procédé en plusieurs étapes impliquant plusieurs intermédiaires clés. Une voie de synthèse courante comprend les étapes suivantes :
Formation de l'intermédiaire I : L'étape initiale implique la réaction du 4-chloro-3-(4-(tétrahydrofuran-3-yloxy)benzyl)phényl avec un donneur de glucosyle approprié pour former l'intermédiaire I.
Formation de l'intermédiaire II : L'intermédiaire I subit d'autres réactions, y compris des étapes de protection et de déprotection, pour produire l'intermédiaire II.
Couplage final : L'intermédiaire II est ensuite couplé à un donneur de glucosyle approprié dans des conditions basiques pour former l'this compound
Méthodes de production industrielle : La production industrielle d'this compound implique généralement une synthèse à grande échelle utilisant des conditions de réaction optimisées pour assurer un rendement élevé et une pureté élevée. Le processus comprend :
Reflux : Le mélange réactionnel est reflué pour faciliter la formation du produit souhaité.
Purification : Le produit brut est purifié en utilisant des techniques telles que la recristallisation et la chromatographie pour obtenir l'this compound avec une pureté élevée
Analyse Des Réactions Chimiques
Types de réactions : L'empagliflozine subit diverses réactions chimiques, notamment :
Hydrolyse : Le composé est susceptible à l'hydrolyse, en particulier dans des conditions acides et basiques.
Réactifs et conditions courants :
Dégradation oxydative : Des réactifs tels que le peroxyde d'hydrogène ou d'autres agents oxydants peuvent induire une dégradation oxydative.
Principaux produits formés :
Produits de dégradation oxydative : Différents produits d'oxydation peuvent être formés, en fonction des conditions spécifiques et des réactifs utilisés.
Produits d'hydrolyse : L'hydrolyse peut conduire à la formation de fragments plus petits et de produits de dégradation.
4. Applications de la recherche scientifique
L'this compound a un large éventail d'applications de recherche scientifique, notamment :
Gestion du diabète : L'this compound est principalement utilisée pour gérer le diabète de type 2 en abaissant le taux de sucre dans le sang
Avantages cardiovasculaires : La recherche a montré que l'this compound peut réduire le risque d'événements cardiovasculaires, tels que les crises cardiaques et les accidents vasculaires cérébraux, chez les patients atteints de diabète de type 2
Protection rénale : L'this compound s'est avérée avoir des effets néphroprotecteurs, réduisant le risque de progression de la maladie rénale.
Insuffisance cardiaque : Le composé est également utilisé pour traiter l'insuffisance cardiaque, offrant des avantages au-delà du contrôle du glucose.
5. Mécanisme d'action
L'this compound exerce ses effets en inhibant le cotransporteur sodium-glucose 2 (SGLT2) dans les reins. Cette inhibition réduit la réabsorption du glucose du filtrat glomérulaire, ce qui entraîne une augmentation de l'excrétion du glucose dans les urines. La réduction du taux de glucose dans le sang aide à gérer le diabète de type 2. De plus, l'this compound s'est avérée avoir des effets cardioprotecteurs et néphroprotecteurs, qui seraient liés à des mécanismes tels que la réduction du stress oxydatif et l'amélioration de la fonction endothéliale .
Comparaison Avec Des Composés Similaires
L'empagliflozine fait partie de la classe des médicaments inhibiteurs du SGLT2. D'autres composés similaires dans cette classe comprennent :
Canagliflozine : Un autre inhibiteur du SGLT2 utilisé pour gérer le diabète de type 2.
Dapagliflozine : Ce composé est également utilisé pour traiter le diabète de type 2 et a été approuvé pour une utilisation dans l'insuffisance cardiaque.
Ertugliflozine : Un autre inhibiteur du SGLT2 ayant des mécanismes d'action similaires mais des propriétés pharmacocinétiques différentes.
Unicité de l'this compound : L'this compound est unique par sa haute sélectivité pour le SGLT2 par rapport au SGLT1, ce qui contribue à son efficacité et à son profil de sécurité. Il a également été démontré qu'il avait des avantages cardiovasculaires et rénaux importants, ce qui en fait une option précieuse pour les patients atteints de diabète de type 2 et de comorbidités .
Propriétés
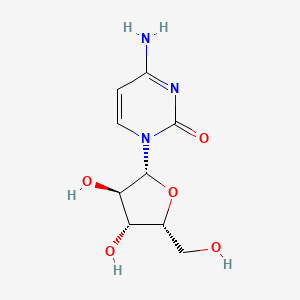
IUPAC Name |
(2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-2-[4-chloro-3-[[4-[(3S)-oxolan-3-yl]oxyphenyl]methyl]phenyl]-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C23H27ClO7/c24-18-6-3-14(23-22(28)21(27)20(26)19(11-25)31-23)10-15(18)9-13-1-4-16(5-2-13)30-17-7-8-29-12-17/h1-6,10,17,19-23,25-28H,7-9,11-12H2/t17-,19+,20+,21-,22+,23-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
OBWASQILIWPZMG-QZMOQZSNSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1COCC1OC2=CC=C(C=C2)CC3=C(C=CC(=C3)C4C(C(C(C(O4)CO)O)O)O)Cl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C1COC[C@H]1OC2=CC=C(C=C2)CC3=C(C=CC(=C3)[C@H]4[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O4)CO)O)O)O)Cl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C23H27ClO7 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID601026093 | |
| Record name | Empagliflozin | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID601026093 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
450.9 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
The vast majority of glucose filtered through the glomerulus is reabsorbed within the proximal tubule, primarily via SGLT2 (sodium-glucose linked co-transporter-2) which is responsible for ~90% of the total glucose reabsorption within the kidneys. Na+/K+-ATPase on the basolateral membrane of proximal tubular cells utilize ATP to actively pump Na+ ions into the interstitium surrounding the tubule, establishing a Na+ gradient within the tubular cell. SGLT2 on the apical membrane of these cells then utilize this gradient to facilitate secondary active co-transport of both Na+ and glucose out of the filtrate, thereby reabsorbing glucose back into the blood – inhibiting this co-transport, then, allows for a marked increase in glucosuria and decrease in blood glucose levels. Empagliflozin is a potent inhibitor of renal SGLT2 transporters located in the proximal tubules of the kidneys and works to lower blood glucose levels via an increase in glucosuria. Empagliflozin also appears to exert cardiovascular benefits - specifically in the prevention of heart failure - independent of its blood glucose-lowering effects, though the exact mechanism of this benefit is not precisely understood. Several theories have been posited, including the potential inhibition of Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE) 1 in the myocardium and NHE3 in the proximal tubule, reduction of pre-load via diuretic/natriuretic effects and reduction of blood pressure, prevention of cardiac fibrosis via suppression of pro-fibrotic markers, and reduction of pro-inflammatory adipokines. | |
| Record name | Empagliflozin | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09038 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
864070-44-0 | |
| Record name | Empagliflozin | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=864070-44-0 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Empagliflozin [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0864070440 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Empagliflozin | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09038 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Empagliflozin | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID601026093 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | (2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-2-(4-chloro-3-(4-((S)-tetrahydrofuran-3-yloxy)benzyl)phenyl)-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | EMPAGLIFLOZIN | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/HDC1R2M35U | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Avertissement et informations sur les produits de recherche in vitro
Veuillez noter que tous les articles et informations sur les produits présentés sur BenchChem sont destinés uniquement à des fins informatives. Les produits disponibles à l'achat sur BenchChem sont spécifiquement conçus pour des études in vitro, qui sont réalisées en dehors des organismes vivants. Les études in vitro, dérivées du terme latin "in verre", impliquent des expériences réalisées dans des environnements de laboratoire contrôlés à l'aide de cellules ou de tissus. Il est important de noter que ces produits ne sont pas classés comme médicaments et n'ont pas reçu l'approbation de la FDA pour la prévention, le traitement ou la guérison de toute condition médicale, affection ou maladie. Nous devons souligner que toute forme d'introduction corporelle de ces produits chez les humains ou les animaux est strictement interdite par la loi. Il est essentiel de respecter ces directives pour assurer la conformité aux normes légales et éthiques en matière de recherche et d'expérimentation.


-lambda5](/img/structure/B1684246.png)
![1-Ethyl-4-[(1E,3E,5E,7E,9E,11E,13E,15E,17E)-18-(1-ethylpyridin-1-ium-4-yl)-3,7,12,16-tetramethyloctadeca-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17-nonaenyl]pyridin-1-ium;dibromide](/img/structure/B1684252.png)
![2-[3-Cyano-5-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,5-dimethylfuran-2-ylidene]propanedinitrile](/img/structure/B1684258.png)
